Appearance of tolerance-induction and non-inflammatory SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after COVID-19 booster vaccinations
- PMID: 38173725
- PMCID: PMC10763240
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1309997
Appearance of tolerance-induction and non-inflammatory SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after COVID-19 booster vaccinations
Abstract
Background: Understanding the characteristics of the humoral immune responses following COVID-19 vaccinations is crucial for refining vaccination strategies and predicting immune responses to emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Methods: A longitudinal analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain (RBD) specific IgG antibody responses, encompassing IgG subclasses IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 was performed. Participants received four mRNA vaccine doses (group 1; n=10) or two ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and two mRNA booster doses (group 2; n=19) in Bangladesh over two years.
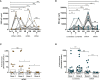
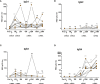
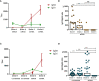
Results: Findings demonstrate robust IgG responses after primary Covishield or mRNA doses; declining to baseline within six months. First mRNA booster restored and surpassed primary IgG responses but waned after six months. Surprisingly, a second mRNA booster did not increase IgG levels further. Comprehensive IgG subclass analysis showed primary Covishield/mRNA vaccination generated predominantly IgG1 responses with limited IgG2/IgG3, Remarkably, IgG4 responses exhibited a distinct pattern. IgG4 remained undetectable initially but increased extensively six months after the second mRNA dose, eventually replacing IgG1 after the 3rd/4th mRNA doses. Conversely, initial Covishield recipients lack IgG4, surged post-second mRNA booster. Notably, mRNA-vaccinated individuals displayed earlier, robust IgG4 levels post first mRNA booster versus Covishield counterparts. IgG1 to IgG4 ratios decreased with increasing doses, most pronounced with four mRNA doses. This study highlights IgG response kinetics, influenced by vaccine type and doses, impacting immunological tolerance and IgG4 induction, shaping future vaccination strategies.
Conclusions: This study highlights the dynamics of IgG responses dependent on vaccine type and number of doses, leading to immunological tolerance and IgG4 induction, and shaping future vaccination strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgG; IgG4; antibody; booster; tolerance; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 Akhtar, Islam, Khaton, Soltana, Jafrin, Rahman, Tauheed, Ahmed, Khan, Akter, Khan, Islam, Khanam, Biswas, Ahmmed, Ahmed, Rashid, Hossain, Alam, Alamgir, Rahman, Ryan, Harris, LaRocque, Flora, Chowdhury, Khan, Banu, Shirin, Bhuiyan and Qadri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker (2023). Available at: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/country/Bangladesh/.
-
- Rahmani K, Shavaleh R, Forouhi M, Disfani HF, Kamandi M, Oskooi RK, et al. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in reducing the incidence, hospitalization, and mortality from COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health (2022) 10:873596. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.873596 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khanam F, Islam MT, Ahmmed F, Ahmed SU, Hossen MI, Rajib MH, et al. Measuring the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines used during a surge of the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 in Bangladesh: A test-negative design evaluation. Vaccines (2022) 10(12):2069. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122069 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

