Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of Chagas cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 38173812
- PMCID: PMC10762800
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250029
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of Chagas cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Chagas cardiomyopathy (CHCM) is the most important clinical manifestation of Chagas disease. The analysis of cardiac miRNAs may contribute to predicting the progression to CHCM in Chagas indeterminate phase and/or to the differential diagnosis for cardiomyopathy.
Methods: We carried out a case-control study to identify circulating miRNAs associated with CHCM. We assigned 104 participants to four groups: healthy controls (HC), Chagas non-cardiomyopathy controls, CHCM cases, and ischemic cardiomyopathy controls. We performed a clinical, echocardiographic, and laboratory evaluation and profiled circulating miRNA in the serum samples.
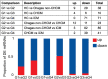
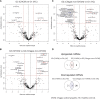
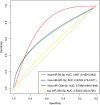
Results: Differences between groups were observed in clinical variables and in the analysis of miRNAs. Compared to HC, CHCM participants had 4 over-expressed and 6 under-expressed miRNAs; miR-95-3p and miR-130b-3p were upregulated in CHCM compared with controls, Chagas non-cardiomyopathy and ischemic cardiomyopathy participants, suggesting that might be a hallmark of CHCM. Analysis of gene targets associated with cardiac injury yielded results of genes involved in arrhythmia generation, cardiomegaly, and hypertrophy.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the expression of circulating miRNAs identified by deep sequencing in CHCM could be associated with different cardiac phenotypes in CHCM subjects, compared with Chagas non-CHCM, ischemic cardiomyopathy controls, and healthy controls.
Keywords: Chagas cardiomyopathy; Chagas disease; biomarkers; circulating microRNAs; microRNAs.
© 2023 Antonietti, Mariani, Martínez, Santalla, Vensentini, Kyle, de Abreu, Tajer, Lacunza and Ferrero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unraveling the role of miRNAs as biomarkers in Chagas cardiomyopathy: Insights into molecular pathophysiology.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Feb 1;18(2):e0011865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011865. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38300899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers Associated with Cardiac Remodeling and Fibrosis in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 20;20(16):4064. doi: 10.3390/ijms20164064. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31434314 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of chronic Chagas heart disease via a small RNA-Seq approach.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 12;14(1):1187. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51487-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38216639 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving a parsimonious cardiac endpoint for use in epidemiological studies of Chagas disease: results from the Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study-II (REDS-II) cohort.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021 Apr 23;63:e31. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202163031. eCollection 2021. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021. PMID: 33909845 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Current State of the Art.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(36):7400-7412. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210405122703. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33820510 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

