Scirpusin B isolated from Passiflora edulis Var. flavicarpa attenuates carbohydrate digestive enzymes, pathogenic bacteria and oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38173823
- PMCID: PMC10758380
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03876-6
Scirpusin B isolated from Passiflora edulis Var. flavicarpa attenuates carbohydrate digestive enzymes, pathogenic bacteria and oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
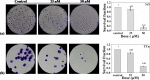
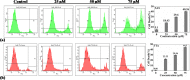
Passiflora edulis Var. flavicarpa (passion fruit) generates vast waste (60-70%) in the form of peel and seed after the juice extraction. The study aimed to isolate Scirpusin B (SB) from passion fruit (PF) seed waste collected from Northeast India and to analyse its anti-radical, antibacterial, anti-diabetic, and anti-oral cancer activities. Scirpusin B was isolated following hydro-alcoholic extraction, fractionation, and column chromatography. The isolated fraction was further identified through NMR and mass spectroscopy. SB exhibited significant antiradical activity against six standard antioxidant compounds, indicating its commercial application. SB inhibited α-amylase (IC50 Value: 76.38 ± 0.25 µg/mL) and α-glucosidase digestive enzymes (IC50 Value: 2.32 ± 0.04 µg/mL), signifying its antidiabetic properties. In addition, SB showed profound antibacterial activity against eight gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria reported for the first time. Furthermore, SB inhibited SAS and TTN oral cancer cell proliferation up to 95% and 83%, respectively. SB significantly inhibited colonies of SAS and TTn cells in the clonogenic assay, attributing to its anticancer properties. The PI-FACS assay confirmed the ability of SB (75 µM) to kill SAS and TTn cells by 40.26 and 44.3% in 72 h. The mechanism of SB inhibiting oral cancer cell proliferation was understood through western blot analysis, where SB significantly suppressed different cancer hallmark proteins, such as TNF-α, survivin, COX-2, cyclin D1, and VEGF-A. The present study suggests that SB isolated from PF seed can add noteworthy value to the waste biomass for various industrial and medical applications.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03876-6.
Keywords: Antibacterial agent; Northeast India; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Passiflora edulis Var. flavicarpa seed; Preparative HPLC; Scirpusin B.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest for this publication.
Figures





References
-
- Arias-Lamos D, Molina-Hernández JB, Andrade-Mahecha MM (2019) Evaluation of the potential use of passion fruit dehydrated epicarp (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa O. Deg.) in the formulation of yogurt. Revista UDCA Actualidad & Divulgación Científica 22 (1)
-
- Aswathy M, Banik K, Parama D, Sasikumar P, Harsha C, Joseph AG, Sherin DR, Thanathu MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Vasu RK. Exploring the cytotoxic effects of the extracts and bioactive triterpenoids from Dillenia indica against oral squamous cell carcinoma: a scientific interpretation and validation of indigenous knowledge. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021;4(2):834–847. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babu B, Jayram H, Nair M, Ajaikumar K, Padikkala J. Free radical scavenging, antitumor and anticarcinogenic activity of gossypin. J Exp Clin Cancer CR. 2003;22(4):581–589. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

