Exploring the psychosocial characteristics of women with gambling disorder through a qualitative study
- PMID: 38173857
- PMCID: PMC10761503
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1294149
Exploring the psychosocial characteristics of women with gambling disorder through a qualitative study
Abstract
Introduction: Gambling disorder is a behavioral addiction that has been primarily male, but in the last few years, the age of onset has been equated between the sexes. The profile of female gamblers could be different from that of men. Consequently, this study analyzes the testimonies of women with gambling disorder to determine their specific characteristics (gambling motives, gambling preferences, and associated pathologies).
Method: The sample comprises 18 women with gambling disorder aged between 30 and 68. Three discussion groups were held, and a "blind" inductive process was carried out to extract categories. The Atlas.Ti 22.0 program was used to recode and analyze the data.
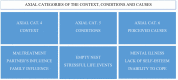
Results: Results show that women may start gambling due to abuse suffered in childhood, and often family members initiate women into gambling. Likewise, the onset of gambling could be a maladaptive way to manage negative emotions. Also highlighted is the predominance of feelings of social stigmatization, which can be reflected in women's choice of games where they are not visible. Comorbidity with other disorders such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, personality disorders, and the use of other substances are noteworthy.
Discussion: The factors explaining why female gamblers do not seek treatment compared to male gamblers are analyzed. More studies on women's experience with gambling are needed to address the specific characteristics of gambling disorder in women.
Keywords: gambling; gender perspective; qualitative; social stigmatization; women.
Copyright © 2023 Estévez, Macía, Ontalvilla and Aurrekoetxea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Psychopathology in online pathological gamblers: a preliminary study].Encephale. 2012 Apr;38(2):156-63. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.01.009. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 22516274 French.
-
Comorbidity, family history and personality traits in pathological gamblers compared with healthy controls.Eur Psychiatry. 2017 May;42:120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Eur Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28364687
-
Psychological Characteristics of Problem Gamblers With and Without Mood Disorder.Can J Psychiatry. 2015 Aug;60(8):369-76. doi: 10.1177/070674371506000806. Can J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26454559 Free PMC article.
-
[Women and gambling: an overview].Recenti Prog Med. 2013 Dec;104(12):631-6. doi: 10.1701/1373.15265. Recenti Prog Med. 2013. PMID: 24362832 Review. Italian.
-
[Types of pathological gamblers].Psychiatr Hung. 2009;24(4):238-47. Psychiatr Hung. 2009. PMID: 19949242 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
A familial subtype of gambling disorder.J Behav Addict. 2024 Aug 13;13(3):761-767. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00042. Print 2024 Oct 4. J Behav Addict. 2024. PMID: 39141440 Free PMC article.
-
Gambling Disorder and Romantic Relationships: The role of positive communication and emotional dysregulation in couple satisfaction.J Gambl Stud. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s10899-025-10410-1. Online ahead of print. J Gambl Stud. 2025. PMID: 40586831
-
Stigmatisation of people experiencing gambling-related harms: a vignette study of the predictors of desire for social distance.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1613798. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1613798. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40606865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althaus J., Zendle D., Bowden-Jones H. (2021). “Gambling and gaming addictions in women” in Textbook of addiction treatment. eds. Carrà G., Galanter M., Baldacchino A. M. (Cham: Springer; )
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders-text revision. 5th Edn. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

