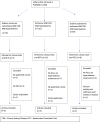
Therapeutic update on oral potassium exchange resin use in chronic kidney disease patients: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials
- PMID: 38173862
- PMCID: PMC10761527
- DOI: 10.3389/jpps.2023.11892
Therapeutic update on oral potassium exchange resin use in chronic kidney disease patients: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials
Abstract
Hyperkalemia is a common electrolyte disorder in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) that increases in prevalence with the decline of glomerular fltration rate (GFR). Another risk of hyperkalemia is the use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors (RAASi) and/or mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) in managing CKD and proteinuria. The treatment of chronic hyperkalemia is challenging especially for outpatients. Treatment options for hyperkalemia include the potassium exchange resins of which two new potassium binders, Patiromer Sorbitex Calcium, and Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate (SZC) have demonstrated their clinical efficacy in reducing serum potassium with a positive safety profile. The old potassium exchange resin sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate™) has some negative side effects including colonic necrosis, hypomagnesemia, and hypernatremia. In this review and literature search, we compare the available oral potassium exchange resins, highlight their advantages and disadvantages and comment on efficacy and safety parameters specifically in CKD patients.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; hyperkalemia; patiromer; sodium polystyrene sulfonate; sodium zirconium cyclosilicate.
Copyright © 2023 Gruver, Al-Makki and Shepler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitor Dosing After Initiation of Outpatient Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate Therapy: The GALVANIZE RAASi Real-World Evidence Study.Adv Ther. 2025 Aug;42(8):3960-3977. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03254-z. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40531443 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of potassium binders in the treatment of patients with chronic kidney disease and hyperkalemia.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;931:175174. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175174. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35964658
-
Novel Potassium Binders in Reduction of Hyperkalemia and Optimization of RAAS Inhibitors Treatment in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease or Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Drugs. 2025 Aug;85(8):1013-1031. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02198-6. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40542996 Free PMC article.
-
Guideline-Recommended Disease-Modifying Therapies for Patients with Cardiorenal Disease: A Call-to-Action Narrative Review.Adv Ther. 2025 Jul;42(7):3141-3157. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03228-1. Epub 2025 May 28. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40434618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperkalemia in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Implications and Management.Heart Fail Rev. 2025 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10741-025-10549-4. Online ahead of print. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 40841869 Review.
References
-
- Kayexalate Package Insert. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate, USP (2009). Avaliable at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/011287s022lbl.pdf (Accessed July 11, 2023).
-
- Patiromer Package Insert. Veltassa (2023). Avaliable at: https://veltassa.com/hcp/pi (Accessed July 5, 2023).
-
- Lokelma Package Insert. Lokelma (2018). Avaliable at: https://den8dhaj6zs0e.cloudfront.net/50fd68b9-106b-4550-b5d0-12b045f8b18... (Accessed July 21, 2023).