Crohn's-related enterocutaneous fistula: a unique cause of penile prosthesis infection
- PMID: 38174017
- PMCID: PMC10761174
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2023.2281214
Crohn's-related enterocutaneous fistula: a unique cause of penile prosthesis infection
Abstract
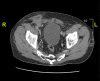
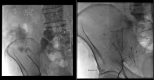
Genitourinary manifestations are rare in patients with Crohn's disease, and a small percentage of patients will experience enterocutaneous fistulas. Infection is one of the most common complications associated with inflatable penile prosthesis placement, which can be associated with fistula formation. In this report, we present a patient with Crohn's disease who developed an inflatable penile prosthesis infection secondary to an undiagnosed enterocutaneous fistula.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; fistula; infection; inflatable penile prosthesis.
Copyright © 2023 Baylor University Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no funding or conflicts of interests. The patient consented in writing to publication of medical information and photographs.
Figures
References
-
- Boussourra H, Sataa S, Rajhi H, Menif N.. Scrotal swelling and penile fistula in a patient with Crohn’s disease. UIJ. 2012;05(03):1–4. doi:10.3834/uij.1944-5784.2012.06.12. - DOI
-
- Smith JA, Howards SS, Dmochowski RR, Hinman F, Preminger GM.. Inflatable penile prosthesis implantation. In: Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:890–899.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources