Exploring Residue-Level Interactions between the Biofilm-Driving R2ab Protein and Polystyrene Nanoparticles
- PMID: 38174900
- PMCID: PMC10843815
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02609
Exploring Residue-Level Interactions between the Biofilm-Driving R2ab Protein and Polystyrene Nanoparticles
Abstract
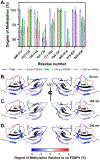
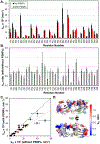
In biological systems, proteins can bind to nanoparticles to form a "corona" of adsorbed molecules. The nanoparticle corona is of significant interest because it impacts an organism's response to a nanomaterial. Understanding the corona requires knowledge of protein structure, orientation, and dynamics at the surface. A residue-level mapping of protein behavior on nanoparticle surfaces is needed, but this mapping is difficult to obtain with traditional approaches. Here, we have investigated the interaction between R2ab and polystyrene nanoparticles (PSNPs) at the level of individual residues. R2ab is a bacterial surface protein from Staphylococcus epidermidis and is known to interact strongly with polystyrene, leading to biofilm formation. We have used mass spectrometry after lysine methylation and hydrogen-deuterium exchange (HDX) NMR spectroscopy to understand how the R2ab protein interacts with PSNPs of different sizes. Lysine methylation experiments reveal subtle but statistically significant changes in methylation patterns in the presence of PSNPs, indicating altered protein surface accessibility. HDX rates become slower overall in the presence of PSNPs. However, some regions of the R2ab protein exhibit faster than average exchange rates in the presence of PSNPs, while others are slower than the average behavior, suggesting conformational changes upon binding. HDX rates and methylation ratios support a recently proposed "adsorbotope" model for PSNPs, wherein adsorbed proteins consist of unfolded anchor points interspersed with partially structured regions. Our data also highlight the challenges of characterizing complex protein-nanoparticle interactions using these techniques, such as fast exchange rates. While providing insights into how R2ab adsorbs onto PSNP surfaces, this research emphasizes the need for advanced methods to comprehend residue-level interactions in the nanoparticle corona.
Figures
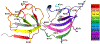

Update of
-
Exploring the Residue-Level Interactions between the R2ab Protein and Polystyrene Nanoparticles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 19:2023.08.28.554951. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.28.554951. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Langmuir. 2024 Jan 16;40(2):1213-1222. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02609. PMID: 37693402 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Exploring the Residue-Level Interactions between the R2ab Protein and Polystyrene Nanoparticles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 19:2023.08.28.554951. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.28.554951. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Langmuir. 2024 Jan 16;40(2):1213-1222. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02609. PMID: 37693402 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Understanding How Staphylococcal Autolysin Domains Interact With Polystyrene Surfaces.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 19;12:658373. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.658373. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34093472 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Polystyrene Nanoparticles with Supported Lipid Bilayers: Impact of Nanoparticle Size and Protein Corona.Macromol Biosci. 2023 Aug;23(8):e2200464. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202200464. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Macromol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36707930
-
Measuring the hydrogen/deuterium exchange of proteins at high spatial resolution by mass spectrometry: overcoming gas-phase hydrogen/deuterium scrambling.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):3018-27. doi: 10.1021/ar500194w. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25171396 Review.
-
Molecular Modeling of Protein Corona Formation and Its Interactions with Nanoparticles and Cell Membranes for Nanomedicine Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 29;13(5):637. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050637. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33947090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kokkinopoulou M; Simon J; Mailaender V; Lieberwirth I; Landfester K Characterizing the Protein Corona of Polystyrene Nanoparticles. In European Microscopy Congress 2016: Proceedings; American Cancer Society, 2016; pp 71–72.
-
- Deuker MFS; Mailänder V; Morsbach S; Landfester K Anti-PEG Antibodies Enriched in the Protein Corona of PEGylated Nanocarriers Impact the Cell Uptake. Nanoscale Horiz. 2023, 8, 1377. - PubMed
-
- Walkey CD; Olsen JB; Song F; Liu R; Guo H; Olsen DWH; Cohen Y; Emili A; Chan WCW Protein Corona Fingerprinting Predicts the Cellular Interaction of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8 (3), 2439–2455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

