Within-host evolutionary dynamics and tissue compartmentalization during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 38174928
- PMCID: PMC10805032
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01618-23
Within-host evolutionary dynamics and tissue compartmentalization during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
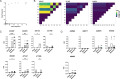
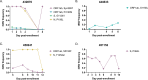
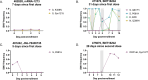
The global evolution of SARS-CoV-2 depends in part upon the evolutionary dynamics within individual hosts with varying immune histories. To characterize the within-host evolution of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, we sequenced saliva and nasal samples collected daily from vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals early during infection. We show that longitudinal sampling facilitates high-confidence genetic variant detection and reveals evolutionary dynamics missed by less-frequent sampling strategies. Within-host dynamics in both unvaccinated and vaccinated individuals appeared largely stochastic; however, in rare cases, minor genetic variants emerged to frequencies sufficient for forward transmission. Finally, we detected significant genetic compartmentalization of viral variants between saliva and nasal swab sample sites in many individuals. Altogether, these data provide a high-resolution profile of within-host SARS-CoV-2 evolutionary dynamics.IMPORTANCEWe detail the within-host evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 during acute infection in 31 individuals using daily longitudinal sampling. We characterized patterns of mutational accumulation for unvaccinated and vaccinated individuals, and observed that temporal variant dynamics in both groups were largely stochastic. Comparison of paired nasal and saliva samples also revealed significant genetic compartmentalization between tissue environments in multiple individuals. Our results demonstrate how selection, genetic drift, and spatial compartmentalization all play important roles in shaping the within-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 populations during acute infection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; genetic compartmentalization; viruses; within-host evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Baang JH, Smith C, Mirabelli C, Valesano AL, Manthei DM, Bachman MA, Wobus CE, Adams M, Washer L, Martin ET, Lauring AS. 2021. Prolonged severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 replication in an immunocompromised patient. J Infect Dis 223:23–27. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa666 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avanzato VA, Matson MJ, Seifert SN, Pryce R, Williamson BN, Anzick SL, Barbian K, Judson SD, Fischer ER, Martens C, Bowden TA, de Wit E, Riedo FX, Munster VJ. 2020. Case study: prolonged infectious SARS-CoV-2 shedding from an asymptomatic immunocompromised individual with cancer. Cell 183:1901–1912. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.049 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

