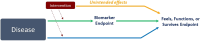
Meaningful Endpoints for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Clinical Trials: Emphasis on 'Feels, Functions, Survives'. Report of a Collaborative Discussion in a Symposium with Direct Engagement from Representatives of Patients, Investigators, the National Institutes of Health, a Patient Advocacy Organization, and a Regulatory Agency
- PMID: 38174955
- PMCID: PMC12039048
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202312-2213SO
Meaningful Endpoints for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Clinical Trials: Emphasis on 'Feels, Functions, Survives'. Report of a Collaborative Discussion in a Symposium with Direct Engagement from Representatives of Patients, Investigators, the National Institutes of Health, a Patient Advocacy Organization, and a Regulatory Agency
Abstract
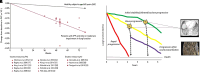
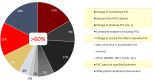
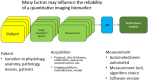
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) carries significant mortality and unpredictable progression, with limited therapeutic options. Designing trials with patient-meaningful endpoints, enhancing the reliability and interpretability of results, and streamlining the regulatory approval process are of critical importance to advancing clinical care in IPF. Methods: A landmark in-person symposium in June 2023 assembled 43 participants from the US and internationally, including patients with IPF, investigators, and regulatory representatives, to discuss the immediate future of IPF clinical trial endpoints. Patient advocates were central to discussions, which evaluated endpoints according to regulatory standards and the FDA's 'feels, functions, survives' criteria. Results: Three themes emerged: 1) consensus on endpoints mirroring the lived experiences of patients with IPF; 2) consideration of replacing forced vital capacity (FVC) as the primary endpoint, potentially by composite endpoints that include 'feels, functions, survives' measures or FVC as components; 3) support for simplified, user-friendly patient-reported outcomes (PROs) as either components of primary composite endpoints or key secondary endpoints, supplemented by functional tests as secondary endpoints and novel biomarkers as supportive measures (FDA Guidance for Industry (Multiple Endpoints in Clinical Trials) available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/162416/download). Conclusions: This report, detailing the proceedings of this pivotal symposium, suggests a potential turning point in designing future IPF clinical trials more attuned to outcomes meaningful to patients, and documents the collective agreement across multidisciplinary stakeholders on the importance of anchoring IPF trial endpoints on real patient experiences-namely, how they feel, function, and survive. There is considerable optimism that clinical care in IPF will progress through trials focused on patient-centric insights, ultimately guiding transformative treatment strategies to enhance patients' quality of life and survival.
Keywords: FVC, 6MWT, composite endpoint for IPF trials; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; image and circulatory biomarkers for IPF trials; meaningful outcomes as endpoints for IPF trials; patient reported outcomes for IPF trials.
Figures

Comment in
-
Assessing How Patients Feel, Function, and Survive in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The Best Is the Enemy of the Good.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Aug 1;210(3):367-368. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202402-0337LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38820300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Podolanczuk AJ, Thomson CC, Remy-Jardin M, Richeldi L, Martinez FJ, Kolb M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: state of the art for 2023. Eur Respir J . 2023;61:2200957. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2011;183:788–824. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Respiratory Society, and Latin American Thoracic Society Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2018;198:e44–e68. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: shifting the concept to irreversible pulmonary fibrosis of many entities. Lancet Respir Med . 2019;7:926–929. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

