Cobalt-catalyzed synthesis of amides from alkenes and amines promoted by light
- PMID: 38175889
- PMCID: PMC10799253
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adk2312
Cobalt-catalyzed synthesis of amides from alkenes and amines promoted by light
Abstract
Catalytic methods to couple alkene and amine feedstocks are valuable in synthetic chemistry. The direct carbonylative coupling of alkenes and amines holds promise as a perfectly atom-economical approach to amide synthesis, but general methods remain underdeveloped. Herein, we report an alkene hydroaminocarbonylation catalyzed by unmodified, inexpensive cobalt carbonyl under mild conditions and low pressure promoted by light. Silane addition after the reaction enables sequential cobalt-catalyzed amide reduction, constituting a formal alkene hydroaminomethylation. These methods exhibit exceptional scope across both alkene and amine components with high chemo- and regioselectivity and proceed efficiently even in the absence of solvent. The formation of a hydridocobalt through photodissociation of a carbonyl ligand is proposed to enable catalytic activity under mild conditions, which addresses a long-standing challenge in catalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


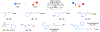


References
-
- Trowbridge A, Walton SM, Gaunt MJ, New Strategies for the Transition-Metal Catalyzed Synthesis of Aliphatic Amines. Chem. Rev 120, 2613–2692 (2020). - PubMed
-
- DiPucchio RC, Rosca S-C, Schafer LL, Hydroaminoalkylation for the Catalytic Addition of Amines to Alkenes or Alkynes: Diverse Mechanisms Enable Diverse Substrate Scope. J. Am. Chem. Soc 144, 11459–11481 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Kalck P, M. Urrutigoïty, Tandem Hydroaminomethylation Reaction to Synthesize Amines from Alkenes. Chem. Rev 118, 3833–3861 (2018). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

