Effectiveness of non-surgical management in rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy (the effect trial): protocol for a randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 38176875
- PMCID: PMC10773347
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-074949
Effectiveness of non-surgical management in rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy (the effect trial): protocol for a randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy (RCCT) involves calcific deposits in the rotator cuff. Non-surgical interventions such as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) and ultrasound-guided percutaneous irrigation of calcific tendinopathy (US-PICT) are recommended for its early management. Exercise therapy (ET) has shown to be an effective intervention for people with rotator cuff tendinopathy, but it has not been formally tested in RCCT. The main objective of this study is to compare the effectiveness of an ET programme with ESWT and US-PICT in people with RCCT. As a secondary aim, this study aims to describe the natural history of RCCT.
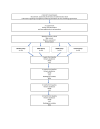
Methods and analysis: A randomised, single-blinded four-group clinical trial will be conducted. Adults from 30 to 75 years diagnosed with RCCT who accomplish eligibility criteria will be recruited. Participants (n=116) will be randomised into four groups: ET group will receive a 12-week rehabilitation programme; ESWT group will receive four sessions with 1 week rest between sessions during 1 month; US-PICT group will receive two sessions with 3 months of rest between sessions; and (actual) wait-and-see group will not receive any intervention during the 12-month follow-up. The primary outcome will be shoulder pain assessed with the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index at baseline, 2 weeks, 4 months, 6 months and 12 months from baseline. The primary analysis will be performed at 12 months from baseline. Secondary outcomes will include pain, range of motion, patient satisfaction and imaging-related variables. Moreover, the following psychosocial questionnaires with their corresponding outcome measure will be assessed: Central Sensitization Inventory (symptoms related to central sensitization); Pain Catastrophizing Scale (pain catastrophizing); Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia 11 items (fear of movement); Fear Avoidance Belief Questionnaire (fear avoidance behaviour); Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (anxiety and depression); Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (sleep quality); and the EuroQol-5D (quality of life). An intention-to-treat analysis will be performed to reduce the risk of bias using a worst-case and best-case scenario analysis.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethics committee approval for this study has been obtained (reference number: 1718862). The results of the main trial will be submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
Trial registration number: NCT05478902.
Keywords: Calcification; Exercise Therapy; Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy; Pain Management; Physical Therapy Modalities; Rehabilitation Medicine; Shoulder Pain.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and kinesio taping in calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018 Jun;54(3):333-340. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.17.04749-9. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018. PMID: 29185674 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing Ultrasound-Guided Needling Combined With a Subacromial Corticosteroid Injection Versus High-Energy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Calcific Tendinitis of the Rotator Cuff: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Arthroscopy. 2020 Jul;36(7):1823-1833.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.02.027. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Arthroscopy. 2020. PMID: 32114063 Clinical Trial.
-
US-guided percutaneous irrigation of calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff in patients with or without previous external shockwave therapy.Radiol Med. 2021 Jan;126(1):117-123. doi: 10.1007/s11547-020-01229-4. Epub 2020 May 25. Radiol Med. 2021. PMID: 32451885
-
Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: a review of operative versus nonoperative management.Phys Sportsmed. 2020 Sep;48(3):241-246. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2019.1710617. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Phys Sportsmed. 2020. PMID: 31893972 Review.
-
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy: from diagnosis to treatment.Acta Biomed. 2018 Jan 19;89(1-S):186-196. doi: 10.23750/abm.v89i1-S.7022. Acta Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29350647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Therapeutic Approaches for Degenerative Tendinopathy: Evaluating Efficacy and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 4;25(21):11846. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111846. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Versus Landmark-Based Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Calcific Shoulder Tendinopathy: An Interventional Clinical Trial.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;15(9):1142. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15091142. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361960 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
