Pyridylpiperazine efflux pump inhibitor boosts in vivo antibiotic efficacy against K. pneumoniae
- PMID: 38177534
- PMCID: PMC10897476
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-023-00007-9
Pyridylpiperazine efflux pump inhibitor boosts in vivo antibiotic efficacy against K. pneumoniae
Abstract
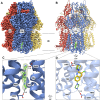
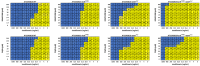
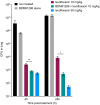
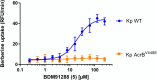
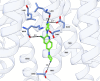
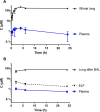
Antimicrobial resistance is a global problem, rendering conventional treatments less effective and requiring innovative strategies to combat this growing threat. The tripartite AcrAB-TolC efflux pump is the dominant constitutive system by which Enterobacterales like Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae extrude antibiotics. Here, we describe the medicinal chemistry development and drug-like properties of BDM91288, a pyridylpiperazine-based AcrB efflux pump inhibitor. In vitro evaluation of BDM91288 confirmed it to potentiate the activity of a panel of antibiotics against K. pneumoniae as well as revert clinically relevant antibiotic resistance mediated by acrAB-tolC overexpression. Using cryo-EM, BDM91288 binding to the transmembrane region of K. pneumoniae AcrB was confirmed, further validating the mechanism of action of this inhibitor. Finally, proof of concept studies demonstrated that oral administration of BDM91288 significantly potentiated the in vivo efficacy of levofloxacin treatment in a murine model of K. pneumoniae lung infection.
Keywords: AcrAB-TolC; Antibiotic Efflux Pump; Antimicrobial Resistance; Cryo-EM; Efflux Pump Inhibitor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AVDC, J-CJ-C, NC, RTM, KMP, MF, NW and RCH are inventors on patent application covering the EPI described in this manuscript. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Zwart PH, Adams PD. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012;68:352–367. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912001308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aulin LBS, Tandar ST, van Zijp T, van Ballegooie E, van der Graaf PH, Saleh MAA, Välitalo P, van Hasselt JGC. Physiologically based modelling framework for prediction of pulmonary pharmacokinetics of antimicrobial target site concentrations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022;61:1735–1748. doi: 10.1007/s40262-022-01186-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belmar Campos C, Aepfelbacher M, Hentschke M. Molecular analysis of the ramRA locus in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates with reduced susceptibility to tigecycline. New Microbiol. 2017;40:135–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- BioProject/PRJNA1017663
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

