Twenty years of participation of racialised groups in type 2 diabetes randomised clinical trials: a meta-epidemiological review
- PMID: 38177564
- PMCID: PMC10844363
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-023-06052-w
Twenty years of participation of racialised groups in type 2 diabetes randomised clinical trials: a meta-epidemiological review
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Type 2 diabetes mellitus prevalence is increasing globally and the greatest burden is borne by racialised people. However, there are concerns that the enrolment of racialised people into RCTs is limited, resulting in a lack of ethnic and racial diversity. This may differ depending whether an RCT is government funded or industry funded. The aim of this study was to review the proportions of racialised and white participants included in large RCTs of type 2 diabetes pharmacotherapies relative to the disease burden of type 2 diabetes in these groups.
Methods: The Ovid MEDLINE database was searched from 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2020. English language reports of RCTs of type 2 diabetes pharmacotherapies published in select medical journals were included. Studies were included in this review if they had a sample size of at least 100 participants and all participants were adults with type 2 diabetes. Industry-funded trials must have recruited participants from at least two countries. Government-funded trials were not held to the same standard because they are typically conducted in a single country. Data including the numbers and proportions of participants by ethnicity and race were extracted from trial reports. The participation-to-prevalence ratio (PPR) was calculated for each trial by dividing the percentage of white and racialised participants in each trial by the percentage of white and racialised participants with type 2 diabetes, respectively, for the regions of recruitment. A random-effects meta-analysis was used to generate the pooled PPRs and 95% CIs across study types. A PPR <0.80 indicates under-representation and a PPR >1.20 indicates over-representation. Risk of bias assessments were not conducted for this study as the objective was to examine recruitment of racialised and white participants rather than evaluate the trustworthiness of clinical trial outcomes.
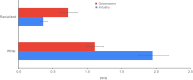
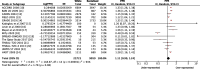
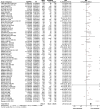
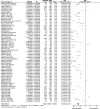
Results: A total of 83 trials were included, involving 283,122 participants, of which 15 were government-funded and 68 were industry-funded trials. In government-funded trials, the PPR for white participants was 1.11 (95% CI 0.99, 1.24) and the PPR for racialised participants was 0.72 (95% CI 0.60, 0.86). In industry-funded trials, the PPR for white participants was 1.95 (95% CI 1.74, 2.18) and the PPR for racialised participants was 0.36 (95% CI 0.32, 0.42). The limitations of this study include the reliance on investigator-reported ethnicity and race to classify participants as 'white' or 'racialised', the use of estimates for type 2 diabetes prevalence and demographic data, and the high levels of heterogeneity of pooled estimates. However, despite these limitations, the results were consistent with respect to direction.
Conclusions/interpretation: Racialised participants are under-represented in government- and industry-funded type 2 diabetes trials. Strategies to improve recruitment and enrolment of racialised participants into RCTs should be developed.
Registration: Open Science Framework registration no. f59mk ( https://osf.io/f59mk ) FUNDING: The authors received no financial support for this research or authorship of the article.
Keywords: Ethnicity; Meta-analysis; RCT; Race; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring ethnic representativeness in diabetes clinical trial enrolment from 2000 to 2020: a chronological survey.Diabetologia. 2022 Sep;65(9):1461-1472. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05736-z. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Diabetologia. 2022. PMID: 35705796 Free PMC article.
-
Inequities in atrial fibrillation trials: An analysis of participant race, ethnicity, and sex over time.Heart Rhythm. 2025 Mar;22(3):602-608. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2024.06.052. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Heart Rhythm. 2025. PMID: 38950875
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Is Our Science Representative? A Systematic Review of Racial and Ethnic Diversity in Orthopaedic Clinical Trials from 2000 to 2020.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022 May 1;480(5):848-858. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002050. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022. PMID: 34855650 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Treatment satisfaction and time in range after 16 weeks of treatment with iGlarLixi in insulin-naive adults with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 May;27(5):2523-2530. doi: 10.1111/dom.16251. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39950217 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of iGlarLixi on continuous glucose monitoring-measured time in range in insulin-naive adults with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Apr;27(4):2173-2182. doi: 10.1111/dom.16214. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39905643 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cross-sectional design and protocol for Artificial Intelligence Ready and Equitable Atlas for Diabetes Insights (AI-READI).BMJ Open. 2025 Feb 6;15(2):e097449. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-097449. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39915016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institutes of Health (2022) Inclusion of women and minorities as participants in research involving human subjects. Available from: https://grants.nih.gov/policy/inclusion/women-and-minorities.htm. Accessed 5 Feb 2023
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

