The NSP3 protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds fragile X mental retardation proteins to disrupt UBAP2L interactions
- PMID: 38177924
- PMCID: PMC10897489
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-023-00043-z
The NSP3 protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds fragile X mental retardation proteins to disrupt UBAP2L interactions
Abstract
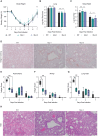
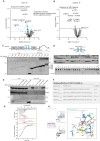
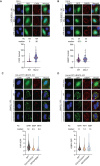
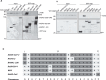
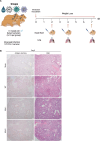
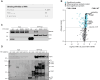
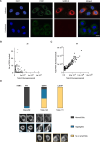
Viruses interact with numerous host factors to facilitate viral replication and to dampen antiviral defense mechanisms. We currently have a limited mechanistic understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 binds host factors and the functional role of these interactions. Here, we uncover a novel interaction between the viral NSP3 protein and the fragile X mental retardation proteins (FMRPs: FMR1, FXR1-2). SARS-CoV-2 NSP3 mutant viruses preventing FMRP binding have attenuated replication in vitro and reduced levels of viral antigen in lungs during the early stages of infection. We show that a unique peptide motif in NSP3 binds directly to the two central KH domains of FMRPs and that this interaction is disrupted by the I304N mutation found in a patient with fragile X syndrome. NSP3 binding to FMRPs disrupts their interaction with the stress granule component UBAP2L through direct competition with a peptide motif in UBAP2L to prevent FMRP incorporation into stress granules. Collectively, our results provide novel insight into how SARS-CoV-2 hijacks host cell proteins and provides molecular insight into the possible underlying molecular defects in fragile X syndrome.
Keywords: Fragile X Syndrome; NSP3; SARS-CoV-2; Stress Granules; UBAP2L.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
VDM has filed a patent on the reverse genetic system and reporter SARS-CoV-2. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

