Preoperative prognostic nutritional index value as a predictive factor for postoperative delirium in older adult patients with hip fractures: a secondary analysis
- PMID: 38178002
- PMCID: PMC10768121
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-023-04629-z
Preoperative prognostic nutritional index value as a predictive factor for postoperative delirium in older adult patients with hip fractures: a secondary analysis
Abstract
Background: Malnutrition is a common geriatric syndrome and can be targeted preoperatively to decrease the risk of postoperative delirium (POD) in older adult patients. To analyze the value of the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) to predict the incidence of POD in older adult patients with hip fractures.
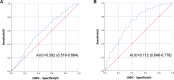
Methods: This was a prospective, observational, cohort study of older adult patients with hip fractures. Preoperative PNI was calculated as 10 × serum albumin (g/dL) + 0.005 × total lymphocyte count (/μL) using preoperative laboratory results. Patients were divided into POD and non-POD groups using the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM). The risk factors associated with POD as well as the relationship between PNI values and the incidence of POD were analyzed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. The predictive value of PNI for POD was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
Results: In this cohort of 369 patients who underwent hip fracture surgery, 67 patients (18.2%) were diagnosed with POD by the CAM results. Low PNI increased the risk of POD (odds ratio (OR) = 0.928, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.864-0.997). General anesthesia (OR = 2.307, 95% CI: 1.279-4.162) and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score (OR = 0.956, 95% CI: 0.920-0.994) were also identified as risk factors for POD. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis suggested that PNI combined with the anesthetic method and MMSE score may be used as a potential predictive indicator of POD after hip fracture surgery.
Conclusion: Preoperative PNI value is related to POD in older adult patients with hip fractures.
Trial registration: This secondary analysis study was approved by the Peking University Third Hospital Medical Science Research Ethics Committee (approval No. M2022578) and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2300070569).
Keywords: Hip fracture; Nutritional status; Older adult patients; Postoperative delirium; Prognostic nutritional index.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li T, Li J, Yuan L, Wu J, Jiang C, Daniels J, Mehta RL, Wang M, Yeung J, Jackson T, Melody T, Jin S, Yao Y, Wu J, Chen J, Smith FG, Lian Q. Effect of regional vs general anesthesia on incidence of postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing hip fracture surgery: the RAGA randomized trial. JAMA. 2022;327:50–58. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.22647. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nomura Y, Nakano M, Bush B, Tian J, Yamaguchi A, Walston J, Hasan R, Zehr K, Mandal K, LaFlam A, Neufeld KJ, Kamath V, Hogue CW, Brown CHt. Observational study examining the association of baseline frailty and postcardiac surgery delirium and cognitive change. Anesth Analg. 2019;129:507–514. doi: 10.1213/ane.0000000000003967. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

