Gut microbiota, circulating cytokines and dementia: a Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38178103
- PMCID: PMC10765696
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-023-02999-0
Gut microbiota, circulating cytokines and dementia: a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Some studies have shown that gut microbiota may be associated with dementia. However, the causal effects between gut microbiota and different types of dementia and whether cytokines act as a mediator remain unclear.
Methods: Gut microbiota, cytokines, and five dementia types, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), dementia with Lewy body (DLB), vascular dementia (VD), and Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD) were identified from large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS) summary data. We used Mendelian randomization (MR) to investigate the causal relationships between gut microbiota, cytokines, and five types of dementia. Inverse variance weighting (IVW) was used as the main statistical method. In addition, we explored whether cytokines act as a mediating factor in the pathway from gut microbiota to dementia.
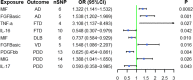
Results: There were 20 positive and 16 negative causal effects between genetic liability in the gut microbiota and dementia. Also, there were five positive and four negative causal effects between cytokines and dementias. Cytokines did not act as mediating factors.
Conclusions: Gut microbiota and cytokines were causally associated with five types of dementia, and cytokines seemed not to be the mediating factors in the pathway from gut microbiota to dementia.
Keywords: Cytokines; Dementia; Gut microbiota; Mendelian randomization.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

