Injectable MSC Spheroid and Microgel Granular Composites for Engineering Tissue
- PMID: 38178647
- PMCID: PMC10994732
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202312226
Injectable MSC Spheroid and Microgel Granular Composites for Engineering Tissue
Abstract
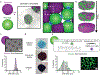
Many cell types require direct cell-cell interactions for differentiation and function; yet, this can be challenging to incorporate into 3-dimensional (3D) structures for the engineering of tissues. Here, a new approach is introduced that combines aggregates of cells (spheroids) with similarly-sized hydrogel particles (microgels) to form granular composites that are injectable, undergo interparticle crosslinking via light for initial stabilization, permit cell-cell contacts for cell signaling, and allow spheroid fusion and growth. One area where this is important is in cartilage tissue engineering, as cell-cell contacts are crucial to chondrogenesis and are missing in many tissue engineering approaches. To address this, granular composites are developed from adult porcine mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) spheroids and hyaluronic acid microgels and simulations and experimental analyses are used to establish the importance of initial MSC spheroid to microgel volume ratios to balance mechanical support with tissue growth. Long-term chondrogenic cultures of granular composites produce engineered cartilage tissue with extensive matrix deposition and mechanical properties within the range of cartilage, as well as integration with native tissue. Altogether, a new strategy of injectable granular composites is developed that leverages the benefits of cell-cell interactions through spheroids with the mechanical stabilization afforded with engineered hydrogels.
Keywords: granular hydrogel; hyaluronic acid; microparticles; spheroids; tissue engineering.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures


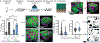


References
-
- DeLise AM, Fischer L, Tuan RS, Osteoarthr. Cartil 2000, 8, 309. - PubMed
-
- Litviňuková M, Talavera-López C, Maatz H, Reichart D, Worth CL, Lindberg EL, Kanda M, Polanski K, Heinig M, Lee M, Nadelmann ER, Roberts K, Tuck L, Fasouli ES, DeLaughter DM, McDonough B, Wakimoto H, Gorham JM, Samari S, Mahbubani KT, Saeb-Parsy K, Patone G, Boyle JJ, Zhang H, Zhang H, Viveiros A, Oudit GY, Bayraktar OA, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Noseda M, Hubner N, Teichmann SA, Nature 2020, 588, 466. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

