Neuroimaging in PRUNE1 syndrome: a mini-review of the literature
- PMID: 38178891
- PMCID: PMC10764560
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1301147
Neuroimaging in PRUNE1 syndrome: a mini-review of the literature
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Neuroimaging in PRUNE1 syndrome: a mini-review of the literature.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1360347. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1360347. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38375463 Free PMC article.
Abstract
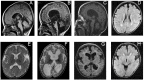
Prune exopolyphosphatase 1 (PRUNE1) is a short-chain phosphatase that is part of the aspartic acid-histidine-histidine (DHH) family of proteins. PRUNE1 is highly expressed in the central nervous system and is crucially involved in neurodevelopment, cytoskeletal rearrangement, cell migration, and proliferation. Recently, biallelic PRUNE1 variants have been identified in patients with neurodevelopmental disorders, hypotonia, microcephaly, variable cerebral anomalies, and other features. PRUNE1 hypomorphic mutations mainly affect the DHH1 domain, leading to an impactful decrease in enzymatic activity with a loss-of-function mechanism. In this review, we explored both the clinical and radiological spectrum related to PRUNE1 pathogenic variants described to date. Specifically, we focused on neuroradiological findings that, together with clinical phenotypes and genetic data, allow us to best characterize affected children with diagnostic and potential prognostic implications.
Keywords: PRUNE1; delayed myelination; enzymatic activity; neurodevelopmental disorder; neurogenesis.
Copyright © 2023 Scorrano, Laura, Spiaggia, Basile, Palmucci, Foti, David, Marinangeli, Mascilini, Comisi, Vittori and Salpietro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

