Bronchial obstruction in osteogenesis imperfecta can be detected by forced oscillation technique
- PMID: 38179272
- PMCID: PMC10764585
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1301873
Bronchial obstruction in osteogenesis imperfecta can be detected by forced oscillation technique
Abstract
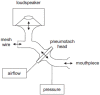
Introduction: Respiratory insufficiency is a leading cause of death in individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). However, evaluating pulmonary function in OI presents challenges. Commonly used pulmonary function tests such as spirometry and body plethysmography are sometimes difficult to perform for OI patients, and reference intervals are not always applicable. The forced oscillation technique (FOT) is a patient-friendly method for detecting respiratory abnormalities that requires no effort from the patient.
Objective: This study investigates the feasibility of FOT in the evaluation of respiratory function in the clinical management of OI patients.
Methods: Twelve OI patients, comprising eight with Sillence OI I, two with OI IV, and two with OI III, underwent spirometry, body plethysmography, and FOT, both pre-and post-administration of salbutamol.
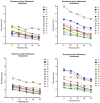
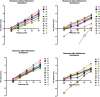
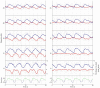
Results: FOT measurements exhibited consistent trends that aligned with spirometry and body plethysmography findings. The resistance at 8 Hz decreased after the administration of salbutamol, indicating that FOT is able to detect bronchial obstruction and its alleviation by medication (p < 0.05). The resonant frequency during expiration was higher than during inspiration in nearly all patients, suggesting obstructive disease. The technique gives insight into both inspiratory and expiratory impairment of pulmonary ventilation. The main FOT parameters showed a relatively high repeatability in duplicate measurements.
Conclusion: Bronchial obstruction can be detected by FOT in patients with OI during quiet breathing, making it an easily executable alternative to other lung function measurements. The technique can detect the bronchodilator effect of sympathomimetic medication. It has the potential to provide information on expiratory flow limitation, pulmonary restriction, and reduced lung compliance.
Keywords: bronchial obstruction; collagen type 1; forced oscillation technique (FOT); lung function; osteogenesis imperfecta (OI).
Copyright © 2023 Storoni, Verdonk, Micha, Jak, Bugiani, Eekhoff and van den Aardweg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Folkestad L. Mortality and morbidity in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta in Denmark. Dan Med J. (2018) 65:B5454. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

