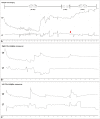
Upbeat and Direction-Changing Torsional Nystagmus While Straight Head Hanging: A New Sign of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Involving Bilateral Posterior Semicircular Canals
- PMID: 38179639
- PMCID: PMC10782080
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2023.0299
Upbeat and Direction-Changing Torsional Nystagmus While Straight Head Hanging: A New Sign of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Involving Bilateral Posterior Semicircular Canals
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ji-Soo Kim serves as an associate editor of Frontiers in Neuro-otology and on the editorial boards of Frontiers in Neuro-ophthalmology, Journal of Neuro-ophthalmology, Journal of Vestibular Research, and Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistent Upbeat Positional Nystagmus in a Patient with Bilateral Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2019 Mar 26;2019:4281641. doi: 10.1155/2019/4281641. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31049238 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics of patients with multi-canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jan-Feb;88(1):89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 32595078 Free PMC article.
-
Congruous Torsional Down Beating Nystagmus in the Third Position of the Semont's Maneuver in Patients Treated for Canalithiasis of Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Its Significance and Prognostic Value.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 15;11:949. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00949. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33071926 Free PMC article.
-
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and its variants.Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;137:241-56. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63437-5.00018-2. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27638076 Review.
-
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022 Oct;49(5):737-747. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2022.03.012. Epub 2022 Apr 3. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022. PMID: 35387740 Review.
References
-
- Karamy B, Zhang H, Archibald J. Systematic review of bilateral benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 2022;132:640–647. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Kim MK, Cho KH, Kim JS. Reversal of initial positioning nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo involving the horizontal canal. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1164:406–408. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

