Statistical Packages and Algorithms for the Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38179940
- PMCID: PMC11571786
- DOI: 10.1177/19322968231221803
Statistical Packages and Algorithms for the Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) measures glucose levels every 1 to 15 minutes and is widely used in clinical and research contexts. Statistical packages and algorithms reduce the time-consuming and error-prone process of manually calculating CGM metrics and contribute to standardizing CGM metrics defined by international consensus. The aim of this systematic review is to summarize existing data on (1) statistical packages for retrospective CGM data analysis and (2) statistical algorithms for retrospective CGM analysis not available in these statistical packages.
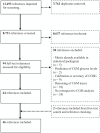
Methods: A systematic literature search in PubMed and EMBASE was conducted on September 19, 2023. We also searched Google Scholar and Google Search until October 12, 2023 as sources of gray literature and performed reference checks of the included literature. Articles in English and Danish were included. This systematic review is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42022378163).
Results: A total of 8731 references were screened and 46 references were included. We identified 23 statistical packages for the analysis of CGM data. The statistical packages could calculate many metrics of the 2022 CGM consensus and non-consensus CGM metrics, and 22/23 (96%) statistical packages were freely available. Also, 23 statistical algorithms were identified. The statistical algorithms could be divided into three groups based on content: (1) CGM data reduction (eg, clustering of CGM data), (2) composite CGM outcomes, and (3) other CGM metrics.
Conclusion: This systematic review provides detailed tabular and textual up-to-date descriptions of the contents of statistical packages and statistical algorithms for retrospective analysis of CGM data.
Keywords: continuous glucose monitoring; statistical algorithms; statistical packages; statistics; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems [the MiniMed® Paradigm™ Veo system and the Vibe™ and G4® PLATINUM CGM (continuous glucose monitoring) system] for managing blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Feb;20(17):v-xxxi, 1-251. doi: 10.3310/hta20170. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 26933827 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous glucose monitoring systems for type 1 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1(1):CD008101. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008101.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258980 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetologia. 2024 May;67(5):798-810. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06107-6. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38363342 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in people living with diabetes and end stage kidney disease on dialysis: a systematic review.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Oct 25;25(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03763-z. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39455937 Free PMC article.
-
Techniques of monitoring blood glucose during pregnancy for women with pre-existing diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 11;6(6):CD009613. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009613.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 23;5:CD009613. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009613.pub4. PMID: 28602020 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Examining Share plus-A Continuous Glucose Monitoring Plus Data-Sharing Intervention in Older Adults and Their Care Partners: Protocol for a Randomized Control Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Dec 16;13:e60004. doi: 10.2196/60004. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39680874 Free PMC article.
-
From data to insights: a tool for comprehensive Quantification of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (QoCGM).PeerJ. 2025 Jun 9;13:e19501. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19501. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40511383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical