Quercetin: a promising virulence inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasB in vitro
- PMID: 38180553
- PMCID: PMC10770215
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-023-12890-w
Quercetin: a promising virulence inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasB in vitro
Abstract
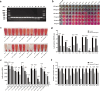
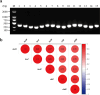
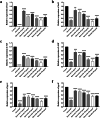
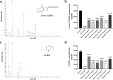
With the inappropriate use of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance has emerged as a major dilemma for patients infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Elastase B (LasB), a crucial extracellular virulence factor secreted by P. aeruginosa, has been identified as a key target for antivirulence therapy. Quercetin, a natural flavonoid, exhibits promising potential as an antivirulence agent. We aim to evaluate the impact of quercetin on P. aeruginosa LasB and elucidate the underlying mechanism. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation revealed a rather favorable intermolecular interaction between quercetin and LasB. At the sub-MICs of ≤256 μg/ml, quercetin was found to effectively inhibit the production and activity of LasB elastase, as well as downregulate the transcription level of the lasB gene in both PAO1 and clinical strains of P. aeruginosa. Through correlation analysis, significant positive correlations were shown between the virulence gene lasB and the QS system regulatory genes lasI, lasR, rhlI, and rhlR in clinical strains of P. aeruginosa. Then, we found the lasB gene expression and LasB activity were significantly deficient in PAO1 ΔlasI and ΔlasIΔrhlI mutants. In addition, quercetin significantly downregulated the expression levels of regulated genes lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, and pqsR as well as effectively attenuated the synthesis of signaling molecules 3-oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL in the QS system of PAO1. Quercetin was also able to compete with the natural ligands OdDHL, BHL, and PQS for binding to the receptor proteins LasR, RhlR, and PqsR, respectively, resulting in the formation of more stabilized complexes. Taken together, quercetin exhibits enormous potential in combating LasB production and activity by disrupting the QS system of P. aeruginosa in vitro, thereby offering an alternative approach for the antivirulence therapy of P. aeruginosa infections. KEY POINTS: • Quercetin diminished the content and activity of LasB elastase of P. aeruginosa. • Quercetin inhibited the QS system activity of P. aeruginosa. • Quercetin acted on LasB based on the QS system.
Keywords: Antivirulence therapy; LasB elastase; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Quercetin; Quorum sensing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



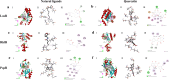
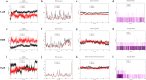
Similar articles
-
Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse peritoneal implant infection model.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 28;12(4):e0176883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176883. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28453568 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing albendazole as a potent inhibitor of quorum sensing-regulated virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel prospects of a classical drug.Microb Pathog. 2024 Jan;186:106468. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106468. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38036112
-
Diallyl disulfide from garlic oil inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors by inactivating key quorum sensing genes.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;102(17):7555-7564. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9175-2. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29951860
-
Inactivation of the quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators LasR or RhlR does not suppress the expression of virulence factors and the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microbiology (Reading). 2019 Apr;165(4):425-432. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000778. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Microbiology (Reading). 2019. PMID: 30707095
-
Mosloflavone attenuates the quorum sensing controlled virulence phenotypes and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: In vitro, in vivo and in silico approach.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jun;131:128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30959097
Cited by
-
Veratryl Alcohol Attenuates the Virulence and Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mainly via Targeting las Quorum-Sensing System.Microorganisms. 2024 May 14;12(5):985. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050985. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792814 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of paeoniflorin on the LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing system and the virulence of Glaesserella parasuis.J Vet Med Sci. 2025 May 15;87(5):565-574. doi: 10.1292/jvms.25-0008. Epub 2025 Mar 31. J Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40159223 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of intestinal pharmacokinetic natural product-drug interactions.Drug Metab Rev. 2024 Aug;56(3):285-301. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2024.2386597. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Drug Metab Rev. 2024. PMID: 39078118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: genetic control mechanisms and therapeutic advances.Mol Biomed. 2024 Nov 27;5(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00221-y. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39592545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Hierarchical Virtual Screening Model for RhlR Inhibitors Based on PCA, Pharmacophore, Docking, and Molecular Dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 22;25(14):8000. doi: 10.3390/ijms25148000. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anju VT, Busi S, Ranganathan S, Ampasala DR, Kumar S, Suchiang K, Kumavath R, Dyavaiah M (2021) Sesamin and sesamolin rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection through the attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence factors. Microb Pathog 155:104912. 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104912 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

