Glomerular filtration rate measurement during platinum treatment for urothelial carcinoma: optimal methods for clinical practice
- PMID: 38180599
- PMCID: PMC10884137
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-023-02454-3
Glomerular filtration rate measurement during platinum treatment for urothelial carcinoma: optimal methods for clinical practice
Abstract
Background: We assessed the accuracy of four estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) methods: MDRD, Cockcroft-Gault, CKD-EPI, and Wright.
Method: The four methods were compared to measure GFR (mGFR) in patients with urothelial urinary tract cancer (T2-T4bNxMx) receiving platinum-based chemotherapy at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, from January 2019 to December 2021. Using standardized assays, creatinine values were measured, and mGFR was determined using Technetium-99 m diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Tc-99 m-DTPA) or Cr-51-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Cr-51-EDTA) plasma clearance. Patients (n = 146) with both mGFR and corresponding creatinine values available were included (n = 345 measurements).
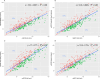
Results: The CKD-EPI method consistently demonstrated superior accuracy, with the lowest Total Deviation Index of 21.8% at baseline and 22.9% for all measurements compared to Wright (23.4% /24.1%), MDRD (26.2%/25.5%), and Cockcroft-Gault (25.x%/25.1%). Bland Altman Limits of agreement (LOA) ranged from - 32 ml/min (Cockcroft-Gault) to + 33 ml/min (MDRD), with CKD-EPI showing the narrowest LOA (- 27 ml/min to + 24 ml/min and lowest bias (0.3 ml/min). Establishing an eGFR threshold at 85 ml/min-considering both the lower limit of agreement (LOA) and the minimum cisplatin limit at 60 ml/min-allows for the safe omission of mGFR in 30% of patients in this cohort.
Conclusion: CKD-EPI equation emerged as the most suitable for estimating kidney function in this patient group although not meeting benchmark criteria. We recommend its use for initial assessment and ongoing monitoring, and suggest mGFR for patients with a CKD-EPI estimated GFR below 85 ml/min. This approach could reduce costs and decrease laboratory time for 30% of our UC patients.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Glomerular filtration rate; Urothelial tract cancer; eGFR; mGFR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DRS: no COI related to this study; speaker honorary, and advisory board on different topics for Jansen, Merck, MSD, Pfizer, BMS; research funding for other trials from Pfizer, Merck. UNJ: no COI related to this study. GD: no COI related to this study. PSO: no COI related to this study. EH: no COI related to this study. JL: no COI related to this study. HP: no COI related to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Performance of Improved Serum Estimators of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) to 99mTc-DTPA GFR Methods in Patients with Hepatic Cirrhosis.J Nucl Med Technol. 2017 Mar;45(1):42-49. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.116.180851. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Nucl Med Technol. 2017. PMID: 28154020 Free PMC article.
-
The Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation does not improve the underestimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) in people with diabetes and preserved renal function.BMC Nephrol. 2015 Dec 3;16:198. doi: 10.1186/s12882-015-0196-0. BMC Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26630928 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients treated with platinum containing therapy.Int J Cancer. 2014 Oct 1;135(7):1733-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28816. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24585507
-
Glomerular filtration rate-estimating equations for patients with advanced chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Oct;28(10):2518-26. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft226. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23904399
-
Glomerular filtration rate: which method should we measure in daily clinical practice?Minerva Med. 2013 Dec;104(6):613-23. Minerva Med. 2013. PMID: 24316914
Cited by
-
Noninvasive assessment of single kidney glomerular filtration rate using multiple diffusion weighted imaging models.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jan;50(1):336-345. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04489-0. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39373771
References
-
- Bamias A, Tzannis K, Harshman LC, et al. Impact of contemporary patterns of chemotherapy utilization on survival in patients with advanced cancer of the urinary tract: a retrospective international study of invasive/advanced cancer of the urothelium (RISC) Ann Oncol. 2018;29:361–369. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx692. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

