The potential value of the Purinergic pathway in the prognostic assessment and clinical application of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38180750
- PMCID: PMC10817410
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205364
The potential value of the Purinergic pathway in the prognostic assessment and clinical application of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
Abstract
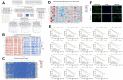
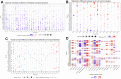
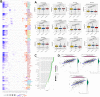
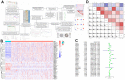
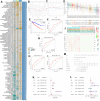
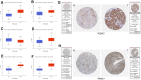
The Purinergic pathway is involved in a variety of important physiological processes in living organisms, and previous studies have shown that aberrant expression of the Purinergic pathway may contribute to the development of a variety of cancers, including kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC). The aim of this study was to delve into the Purinergic pathway in KIRC and to investigate its potential significance in prognostic assessment and clinical treatment. 33 genes associated with the Purinergic pathway were selected for pan-cancer analysis. Cluster analysis, targeted drug sensitivity analysis and immune cell infiltration analysis were applied to explore the mechanism of Purinergic pathway in KIRC. Using the machine learning process, we found that combining the Lasso+survivalSVM algorithm worked well for predicting survival accuracy in KIRC. We used LASSO regression to pinpoint nine Purinergic genes closely linked to KIRC, using them to create a survival model for KIRC. ROC survival curve was analyzed, and this survival model could effectively predict the survival rate of KIRC patients in the next 5, 7 and 10 years. Further univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses revealed that age, grading, staging, and risk scores of KIRC patients were significantly associated with their prognostic survival and were identified as independent risk factors for prognosis. The nomogram tool developed through this study can help physicians accurately assess patient prognosis and provide guidance for developing treatment plans. The results of this study may bring new ideas for optimizing the prognostic assessment and therapeutic approaches for KIRC patients.
Keywords: KIRC; Purinergic; bioinformatics; machine learning; survival model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel prognostic prediction model constructed through machine learning on the basis of methylation-driven genes in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20201604. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201604. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32633782 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of an autophagy-related long noncoding RNA signature for prognosis prediction in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma patients.Cancer Med. 2021 Apr;10(7):2359-2369. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3820. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33650306 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of M7G-related lncRNAs in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and their putative diagnostic and prognostic role.BMC Urol. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01357-9. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 37968670 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small molecule drugs and development of a novel autophagy-related prognostic signature for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Oct;9(19):7034-7051. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3367. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32780567 Free PMC article.
-
An In Silico Investigation of SPC24 as a Putative Biomarker of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma and Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma for Predicting Prognosis and/or Immune Infiltration.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(13):2278-2294. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220315105054. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35293292
Cited by
-
Unraveling the role of ADAMs in clinical heterogeneity and the immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma: insights from single-cell, spatial transcriptomics, and bulk RNA sequencing.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 13;15:1461424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1461424. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39346916 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and therapeutic value of the Eph/Ephrin signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer explored based on bioinformatics.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 31;14(1):17650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68385-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39085301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bedke J, Capitanio U, Dabestani S, Fernández-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Klatte T, Kuusk T, Lam TB, et al.. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. Eur Urol. 2022; 82:399–410. 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.03.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

