Attentional focus strategies in racket sports: A systematic review
- PMID: 38181000
- PMCID: PMC10769023
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285239
Attentional focus strategies in racket sports: A systematic review
Abstract
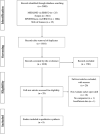
The body of evidence has shown that the external focus of attention (EF) rather than the internal focus of attention (IF) enhances motor skill learning and performance. Within racket sports which require a high level of motor control, anticipation skills, and mental preparedness, effectively directing attention is essential to elicit improvements in athletic performance. The present review aimed to evaluate the scientific evidence concerning the effects of attentional focus instructions on motor learning and performance in racket sports. We systematically reviewed the literature according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The study was registered with the Open Science Framework (osf.io/m4zat). Four electronic databases (Web of Science, Scopus, MEDLINE, and SPORTDiscus) were searched for original research publications. Inclusion criteria were: peer-reviewed journals; healthy and free from injury participants; attentional focus literature specific to the external or internal focus; attentional focus related to motor learning or motor performance; studies included at least one comparator (e.g., different attentional focus group, or control groups with neutral or no specific instruction); publications in which task(s) or skill(s) related to one of the racket sports (tennis, table tennis, badminton, squash, or padel). The initial search yielded 2005 studies. Finally, 9 studies were included in the quantitative analysis. Overall, the results indicated that EF benefits the learning and performance of racket sport skills, compared to IF and over control conditions. The findings suggest that coaches and practitioners should consider the adoption of EF to optimize racket skills performance, particularly in novice or low-skilled athletes.
Copyright: © 2024 Starzak et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pay attention! The influence of coach-, content-, and player-related factors on focus of attention statements during tennis training.Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Jun;23(6):1001-1009. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2022.2056082. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 35343393
-
Quantifying Hitting Load in Racket Sports: A Scoping Review of Key Technologies.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2024 Apr 29;19(6):519-532. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2023-0385. Print 2024 Jun 1. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2024. PMID: 38684208
-
Coincidence-anticipation timing requirements are different in racket sports.Percept Mot Skills. 2012 Oct;115(2):581-93. doi: 10.2466/30.25.27.PMS.115.5.581-593. Percept Mot Skills. 2012. PMID: 23265020
-
Effects of high-intensity interval training on strength, speed, and endurance performance among racket sports players: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 5;19(1):e0295362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295362. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38180964 Free PMC article.
-
Science and the major racket sports: a review.J Sports Sci. 2003 Sep;21(9):707-32. doi: 10.1080/0264041031000140275. J Sports Sci. 2003. PMID: 14579868 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Resistance Training on Sport-Specific Performance of Elite Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.J Hum Kinet. 2024 Apr 15;91(Spec Issue):135-155. doi: 10.5114/jhk/185877. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Hum Kinet. 2024. PMID: 38689584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between hand grip strength and exercise addiction among high-level athletes: differences by sport category and sex in elite athletes.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1597239. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1597239. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40761462 Free PMC article.
-
Padel, pickleball and wellbeing: a systematic review.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 29;16:1614448. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1614448. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40799328 Free PMC article.
-
Physiotherapists' Use of Attentional Focus Instructions and Feedback in the Philippines: A Survey Study.Physiother Res Int. 2025 Apr;30(2):e70035. doi: 10.1002/pri.70035. Physiother Res Int. 2025. PMID: 39921235 Free PMC article.
-
Is holistic focus of attention equally effective to external focus in performing accuracy of table tennis forehand stroke in low-skilled players?BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Apr 11;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01133-2. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40217294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reilly T. The Racquet Sports. Physiology of sports. 1990; 337–369.
-
- Porter J, Wu W, Partridge J. Focus of Attention and Verbal Instructions: Strategies of Elite Track and Field Coaches and Athletes. Sport Science Review. 2010; 19. doi: 10.2478/v10237-011-0018-7 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous