Effect of yoga on cancer-related fatigue in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38181269
- PMCID: PMC10766251
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036468
Effect of yoga on cancer-related fatigue in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a common malignant tumor in women and most patients with breast cancer experience fatigue. Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between yoga and cancer-related fatigue (CRF) in patients with breast cancer. However, these studies drew their conclusions from small sample sizes and lacked sufficient evidence to demonstrate that yoga can effectively alleviate CRF. Therefore, this meta-analysis aims to systematically examine the effects of yoga on cancer fatigue in patients with breast cancer and establish a scientific basis for enhancing their quality of life.
Objective: To assess the effect of yoga on CRF in patients with breast cancer.
Methods: Computer searches were conducted on PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CKNI, and Wanfang databases to retrieve articles related to yoga and CRF in patients with breast cancer from the hospital establishment date to July 2023. The literature was independently screened, and the information was extracted by the researchers. A meta-analysis was conducted using Review Manager Software (version 5.3).
Results: The findings from the meta-analysis of 18 studies indicate that yoga can effectively enhance CFR (standardized mean difference (SMD) = -0.51, 95% confidence interval [CI] = -0.92 to -0.10), improve sleep quality (MD = -3.86, 95%CI = -4.03 to -3.70) in patients with breast cancer, alleviate anxiety and depression (SMD = -0.93, 95%CI = -1.68, -0.18, SMD = -1.23, 95%CI = -2.02 to -0.44), and enhance quality of life (MD = -11.20, 95%CI = -14.16 to -8.24).
Conclusion: Our study offers evidence for the subsequent reduction of CFR in patients with breast cancer. Yoga can alleviate fatigue, improve sleep quality and negative emotions, and improve the quality of life of patients with breast cancer.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

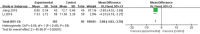



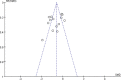
References
-
- Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z, Salehiniya H. Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17:43–6. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler RG, Anderson WF, Gail MH. Increasing breast cancer incidence in China: the numbers add up. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1339–41. - PubMed
-
- Avis NE, Crawford S, Manuel J. Quality of life among younger women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3322–30. - PubMed
-
- Bower JE, Ganz PA, Desmond KA, et al. . Fatigue in breast cancer survivors: occurrence, correlates, and impact on quality of life. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:743–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

