Handling Incomplete or Late-Onset Toxicities in Early-Phase Dose-Finding Clinical Trials: Current Practice and Future Prospects
- PMID: 38181316
- PMCID: PMC10793990
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.23.00441
Handling Incomplete or Late-Onset Toxicities in Early-Phase Dose-Finding Clinical Trials: Current Practice and Future Prospects
Abstract
Purpose: The way late-onset toxicities are managed can affect trial outcomes and participant safety. Specifically, participants often might not have completed their entire follow-up period to observe any toxicities before new participants would be recruited. We conducted a methodological review of published early-phase dose-finding clinical trials that used designs accounting for partial and complete toxicity information, aiming to understand (1) how such designs were implemented and reported and (2) if sufficient information was provided to enable the replicability of trial results.
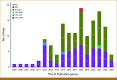
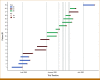
Methods: Until March 26, 2023, we identified 141 trials using the rolling 6 design, the time-to-event continuous reassessment method (TITE-CRM), the TITE-CRM with cycle information, the TITE Bayesian optimal interval design, the TITE cumulative cohort design, and the rapid enrollment design. Clinical settings, design parameters, practical considerations, and dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) information were extracted from these published trials.
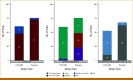
Results: The TITE-CRM (61, 43.3%) and the rolling 6 design (76, 53.9%) were most frequently implemented in practice. Trials using the TITE-CRM had longer DLT assessment windows beyond the first cycle compared with the rolling 6 design (52.5% v 6.6%). Most trials implementing the TITE-CRM (91.8%, 56 of 61) failed to describe essential parameters in the protocols or the study result papers. Only five TITE-CRM trials (8.2%, 5 of 61) reported sufficient information to enable replication of the final analysis.
Conclusion: When compared with trials using the rolling 6 design, those implementing the TITE-CRM design exhibited notable deficiencies in reporting essential details necessary for reproducibility. Inadequate reporting quality of advanced model-based trial designs hinders their credibility. We provide recommendations that can improve transparency, reproducibility, and accurate interpretation of the results for such designs.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
-
- European Medicines Agency : Guideline on the clinical evaluation of anticancer 6 medicinal products. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/draft-guidel...
-
- Cheung YK, Chappell R: Sequential designs for phase I clinical trials with late-onset toxicities. Biometrics 56:1177-1182, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Skolnik JM, Barrett JS, Jayaraman B, et al. : Shortening the timeline of pediatric phase I trials: The rolling six design. J Clin Oncol 26:190-195, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Huang B, Kuan PF: Time-to-event continual reassessment method incorporating treatment cycle information with application to an oncology phase I trial. Biom J 56:933-946, 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

