Mechanosensitive hormone signaling promotes mammary progenitor expansion and breast cancer risk
- PMID: 38181747
- PMCID: PMC11050720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.002
Mechanosensitive hormone signaling promotes mammary progenitor expansion and breast cancer risk
Abstract
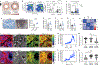
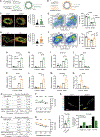
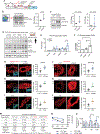
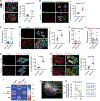
Tissue stem-progenitor cell frequency has been implicated in tumor risk and progression, but tissue-specific factors linking these associations remain ill-defined. We observed that stiff breast tissue from women with high mammographic density, who exhibit increased lifetime risk for breast cancer, associates with abundant stem-progenitor epithelial cells. Using genetically engineered mouse models of elevated integrin mechanosignaling and collagen density, syngeneic manipulations, and spheroid models, we determined that a stiff matrix and high mechanosignaling increase mammary epithelial stem-progenitor cell frequency and enhance tumor initiation in vivo. Augmented tissue mechanics expand stemness by potentiating extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) activity to foster progesterone receptor-dependent RANK signaling. Consistently, we detected elevated phosphorylated ERK and progesterone receptors and increased levels of RANK signaling in stiff breast tissue from women with high mammographic density. The findings link fibrosis and mechanosignaling to stem-progenitor cell frequency and breast cancer risk and causally implicate epidermal growth factor receptor-ERK-dependent hormone signaling in this phenotype.
Keywords: RANK; RANKL; breast cancer risk; extracellular matrix stiffness; integrin signaling; mammary progenitor cells; mammographic density; mechanobiology.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Taube JH, Herschkowitz JI, Komurov K, Zhou AY, Gupta S, Yang J, Hartwell K, Onder TT, Gupta PB, Evans KW, et al. (2010). Core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interactome gene-expression signature is associated with claudin-low and metaplastic breast cancer subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107, 15449–15454. 10.1073/pnas.1004900107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

