The conserved RNA-binding protein Imp is required for the specification and function of olfactory navigation circuitry in Drosophila
- PMID: 38181792
- PMCID: PMC10872534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.12.020
The conserved RNA-binding protein Imp is required for the specification and function of olfactory navigation circuitry in Drosophila
Abstract
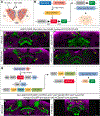
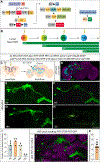
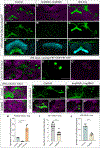
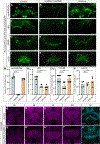
Complex behaviors depend on the precise developmental specification of neuronal circuits, but the relationship between genetic programs for neural development, circuit structure, and behavioral output is often unclear. The central complex (CX) is a conserved sensory-motor integration center in insects, which governs many higher-order behaviors and largely derives from a small number of type II neural stem cells (NSCs). Here, we show that Imp, a conserved IGF-II mRNA-binding protein expressed in type II NSCs, plays a role in specifying essential components of CX olfactory navigation circuitry. We show the following: (1) that multiple components of olfactory navigation circuitry arise from type II NSCs. (2) Manipulating Imp expression in type II NSCs alters the number and morphology of many of these circuit elements, with the most potent effects on neurons targeting the ventral layers of the fan-shaped body (FB). (3) Imp regulates the specification of Tachykinin-expressing ventral FB input neurons. (4) Imp is required in type II NSCs for establishing proper morphology of the CX neuropil structures. (5) Loss of Imp in type II NSCs abolishes upwind orientation to attractive odor while leaving locomotion and odor-evoked regulation of movement intact. Taken together, our findings establish that a temporally expressed gene can regulate the expression of a complex behavior by developmentally regulating the specification of multiple circuit components and provides a first step toward a developmental dissection of the CX and its roles in behavior.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; central complex; neural cell fate; neural circuits; neural identity; neural stem cells; neuropeptides; olfactory navigation; temporal patterning; type II lineages.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
The RNA-binding protein, Imp specifies olfactory navigation circuitry and behavior in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 29:2023.05.26.542522. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.26.542522. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Curr Biol. 2024 Feb 5;34(3):473-488.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.12.020. PMID: 37398350 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Strausfeld NJ (1976). Atlas of an insect brain
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

