Conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care: core components of integrated care for people with kidney failure
- PMID: 38182300
- PMCID: PMC12439246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.001
Conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care: core components of integrated care for people with kidney failure
Abstract
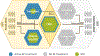
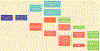
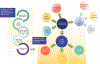
Integrated kidney care requires synergistic linkage between preventative care for people at risk for chronic kidney disease and health services providing care for people with kidney disease, ensuring holistic and coordinated care as people transition between acute and chronic kidney disease and the 3 modalities of kidney failure management: conservative kidney management, transplantation, and dialysis. People with kidney failure have many supportive care needs throughout their illness, regardless of treatment modality. Kidney supportive care is therefore a vital part of this integrated framework, but is nonexistent, poorly developed, and/or poorly integrated with kidney care in many settings, especially in low- and middle-income countries. To address this, the International Society of Nephrology has (i) coordinated the development of consensus definitions of conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care to promote international understanding and awareness of these active treatments; and (ii) identified key considerations for the development and expansion of conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care programs, especially in low resource settings, where access to kidney replacement therapy is restricted or not available. This article presents the definitions for conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care; describes their core components with some illustrative examples to highlight key points; and describes some of the additional considerations for delivering conservative kidney management and kidney supportive care in low resource settings.
Keywords: conservative kidney management; health care policy; integrated kidney care; kidney failure; kidney supportive care.
Copyright © 2023 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All the other authors declared no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Harris DCH, Davies SJ, Finkelstein FO, et al. Increasing access to integrated ESKD care as part of universal health coverage. Kidney Int. 2019;95:S1–S33. - PubMed
-
- Harris DCH, Davies SJ, Finkelstein FO, et al. Strategic plan for integrated care of patients with kidney failure. Kidney Int. 2020;98: S117–S134. - PubMed
-
- Bello AK, Levin A, Lunney M, et al. Status of care for end stage kidney disease in countries and regions worldwide: international cross sectional survey. BMJ (Clin Res ed). 2019;367:l5873. - PubMed
-
- Davison SN, on behalf of the Kidney Supportive Care Research Group. Conservative kidney management care pathway. Accessed June 27, 2023. https://www.ckmcare.com/
-
- St. George Hospital and Community Health Services: renal supportive care. Accessed June 27, 2023. https://stgrenal.org.au/renal-supportivecare
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

