Prognostic model to predict the incidence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38182405
- PMCID: PMC11041610
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-225090
Prognostic model to predict the incidence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: Early diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis (KOA) in asymptomatic stages is essential for the timely management of patients using preventative strategies. We develop and validate a prognostic model useful for predicting the incidence of radiographic KOA (rKOA) in non-radiographic osteoarthritic subjects and stratify individuals at high risk of developing the disease.
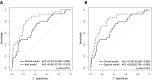
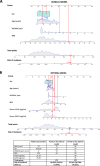
Methods: Subjects without radiographic signs of KOA according to the Kellgren and Lawrence (KL) classification scale (KL=0 in both knees) were enrolled in the OA initiative (OAI) cohort and the Prospective Cohort of A Coruña (PROCOAC). Prognostic models were developed to predict rKOA incidence during a 96-month follow-up period among OAI participants based on clinical variables and serum levels of the candidate protein biomarkers APOA1, APOA4, ZA2G and A2AP. The predictive capability of the biomarkers was assessed based on area under the curve (AUC), and internal validation was performed to correct for overfitting. A nomogram was plotted based on the regression parameters. Model performance was externally validated in the PROCOAC.
Results: 282 participants from the OAI were included in the development dataset. The model built with demographic, anthropometric and clinical data (age, sex, body mass index and WOMAC pain score) showed an AUC=0.702 for predicting rKOA incidence during the follow-up. The inclusion of ZA2G, A2AP and APOA1 data significantly improved the model's sensitivity and predictive performance (AUC=0.831). The simplest model, including only clinical covariates and ZA2G and A2AP serum levels, achieved an AUC=0.826. Both models were internally cross-validated. Predictive performance was externally validated in an independent dataset of 100 individuals from the PROCOAC (AUC=0.713).
Conclusion: A novel prognostic model based on common clinical variables and protein biomarkers was developed and externally validated to predict rKOA incidence over a 96-month period in individuals without any radiographic signs of disease. The resulting nomogram is a useful tool for stratifying high-risk populations and could potentially lead to personalised medicine strategies for treating OA.
Keywords: Chondrocytes; Incidence; Knee Osteoarthritis; Osteoarthritis; Outcome Assessment, Health Care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ on behalf of EULAR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting Incident Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis in Middle-Aged Women Within Four Years: The Importance of Knee-Level Prognostic Factors.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020 Jan;72(1):88-97. doi: 10.1002/acr.23932. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 31127870 Free PMC article.
-
A clinical model including protein biomarkers predicts radiographic knee osteoarthritis: a prospective study using data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021 Aug;29(8):1147-1154. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 33933586
-
Radiomics-based nomogram for predicting total knee replacement in knee osteoarthritis patients.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Jan;182:111854. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111854. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39626336
-
A scoping review of how early-stage knee osteoarthritis has been defined.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023 Sep;31(9):1234-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2023.04.015. Epub 2023 May 22. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023. PMID: 37225053 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging-based biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis outcomes: A narrative review of prediction but not association studies.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Dec;181:111731. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111731. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39276401 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of longitudinal load-bearing tissue MRI radiomics and neural network to predict knee osteoarthritis incidence.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Mar 15;51:187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.01.007. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40144553 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative machine learning frameworks to uncover specific protein signature in neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 10;25(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13454-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39794740 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2024: Molecular biomarkers of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025 Jan;33(1):67-87. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2024.10.003. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 39427749 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

