Vitamin E-enriched medium cross-linked polyethylene in total knee arthroplasty (VIKEP): clinical outcome, oxidation profile, and wear analysis in comparison to standard polyethylene-study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38183062
- PMCID: PMC10768156
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07811-1
Vitamin E-enriched medium cross-linked polyethylene in total knee arthroplasty (VIKEP): clinical outcome, oxidation profile, and wear analysis in comparison to standard polyethylene-study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The gliding surface of total knee endoprostheses is exposed to high loads due to patient weight and activity. These implant components are typically manufactured from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). Crosslinking of UHMWPE by ionizing radiation results in higher wear resistance but induces the formation of free radicals which impair mechanical properties after contact with oxygen. Medium-crosslinked UHMWPE enriched with vitamin E (MXE) provides a balance between the parameters for a sustainable gliding surface, i.e., mechanical strength, wear resistance, particle size, and oxidation stability. Therefore, a gliding surface for knee endoprostheses made up from this material was developed, certified, and launched. The aim of this study is to compare this new gliding surface to the established predecessor in a non-inferiority design.
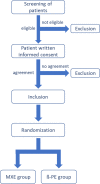
Methods: This multicenter, binational randomized controlled trial will enroll patients with knee osteoarthritis eligible for knee arthroplasty with the index device. Patients will be treated with a knee endoprosthesis with either MXE or a standard gliding surface. Patients will be blinded regarding their treatment. After implantation of the devices, patients will be followed up for 10 years. Besides clinical and patient-related outcomes, radiological data will be collected. In case of revision, the gliding surface will be analyzed biomechanically and regarding the oxidative profile.
Discussion: The comparison between MXE and the standard gliding surface in this study will provide clinical data to confirm preceding biomechanical results in vivo. It is assumed that material-related differences will be identified, i.e., that the new material will be less sensitive to wear and creep. This may become obvious in biomechanical analyses of retrieved implants from revised patients and in radiologic analyses.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04618016. Registered 27 October 2020, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04618016?term=vikep&checkSpell=false&rank=1 . All items from the World Health Organization Trial Registration Data Set can be found in Additional file 1.
Keywords: Clinical study; Gliding surface material; Total knee arthroplasty; UHMWPE.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors filled and provided the ICMJE disclosure form. KM and MS are employees of Aesculap AG. AH declares that she has no conflict of interest. IK and MM declare that they received study grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG for the conduction of this study and received support for attending/traveling to meetings from B.Braun/Aesculap AG. MH and OH declare that they received study grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG for the conduction of this study and received honoraria for various lectures, workshops, and courses from B.Braun/Aesculap AG. JK declares that she received study grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG for the conduction of this study and has an advisor contract for another study sponsored by B.Braun/Aesculap AG and received payments for a congress lecture and received support for attending/traveling to meetings from B.Braun/Aesculap AG. CL and WM declare that they received research grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG and received support for attending/traveling to meetings from B.Braun/Aesculap AG. PM declares that he receives royalties/licenses from X.Nov and Adler. AN declares that he received study grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG for the conduction of this study. BRD declares that he received study grants from B.Braun/Aesculap AG for the conduction of this study and received consulting fees from B.Braun/Aesculap AG and received support for attending/traveling to meetings from Leo Pharma.
Similar articles
-
Vitamin E stabilised polyethylene for total knee arthroplasty evaluated under highly demanding activities wear simulation.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 15;48:415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.031. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27789345
-
Creep and Wear in Vitamin E-Infused Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene Cups for Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Jan 17;100(2):107-114. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.16.01379. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018. PMID: 29342060 Clinical Trial.
-
A multicenter approach evaluating the impact of vitamin e-blended polyethylene in cementless total hip replacement.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2014 Apr 22;6(2):5285. doi: 10.4081/or.2014.5285. eCollection 2014 Apr 22. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2014. PMID: 25002933 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene in Hip and Knee Arthroplasties.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;16(6):2140. doi: 10.3390/ma16062140. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antioxidant and non-antioxidant contributions of vitamin E in vitamin E blended ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for total knee replacement.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014 Mar;31:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 29. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014. PMID: 23369759 Review.
References
-
- Grimberg A, Lützner J, Melsheimer O, Morlock M, Steinbrück A. Jahresbericht 2022: Mit Sicherheit mehr Qualität. 2022. Berlin: EPRD Deutsche Endoprothesenregister; 2022.
-
- Lambert B, Neut D, van der Veen HC, Bulstra SK. Effects of vitamin E incorporation in polyethylene on oxidative degradation, wear rates, immune response, and infections in total joint arthroplasty: a review of the current literature. Int Orthop. 2019;43(7):1549–1557. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4237-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical