Multiplexed miRNA and Protein Analysis Using Digital Quantitative PCR in Microwell Arrays
- PMID: 38183281
- PMCID: PMC11168192
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05213
Multiplexed miRNA and Protein Analysis Using Digital Quantitative PCR in Microwell Arrays
Abstract
Proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs) act in tandem within biological pathways to regulate cellular functions, and their misregulation has been correlated to numerous diseases. Because of their interconnectedness, both miRNAs and proteins must be evaluated together to obtain accurate insights into the molecular pathways of pathogenesis. However, few analytical techniques can measure both classes of biomolecules in parallel from a single biological sample. Here, microfluidic digital quantitative PCR (dqPCR) was developed to simultaneously quantify miRNA and protein targets in a multiplexed assay using a single detection chemistry. This streamlined analysis was achieved by integrating base-stacking PCR and immuno-PCR in a microfluidic array platform. Analyses of let-7a (miRNA) and IL-6 (protein) were first optimized separately to identify thermocycling and capture conditions amenable to both biomolecules. Singleplex dqPCR studies exhibited the expected digital signals and quantification cycles for both analytes over a range of concentrations. Multiplexed analyses were then conducted to quantify both let-7a and IL-6 with high sensitivity (LODs ∼ 3 fM) over a broad dynamic range (5-5000 fM) using only standard PCR reagents. This multiplexed dqPCR was then translated to the analysis of HEK293 cell lysate, where endogenous let-7a and IL-6 were measured simultaneously without sample purification or pretreatment. Collectively, these studies demonstrate that the integration of BS-PCR and immuno-PCR achieves a sensitive and streamlined approach for multiplexed analyses of miRNAs and proteins, which will enable researchers to gain better insights into disease pathogenesis in future applications.
Figures
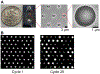
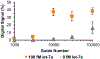

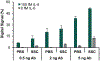


Similar articles
-
Reverse transcription-free digital-quantitative-PCR for microRNA analysis.Analyst. 2023 Jun 26;148(13):3019-3027. doi: 10.1039/d3an00351e. Analyst. 2023. PMID: 37264955 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed and accurate quantification strategy for miRNA based on specific terminal-mediated PCR with equivalent amplification.Talanta. 2023 Jun 1;258:124463. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124463. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 36940574
-
Label-Free and Multiplexed Quantification of microRNAs by Mass Spectrometry Based on Duplex-Specific-Nuclease-Assisted Recycling Amplification.Anal Chem. 2019 Feb 5;91(3):2120-2127. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04583. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30585725
-
Isothermal Amplification for MicroRNA Detection: From the Test Tube to the Cell.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Apr 18;50(4):1059-1068. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00040. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28355077 Review.
-
Digital biology and chemistry.Lab Chip. 2014 Sep 7;14(17):3225-32. doi: 10.1039/c4lc00248b. Lab Chip. 2014. PMID: 24889331 Review.
Cited by
-
Digital PCR: from early developments to its future application in clinics.Lab Chip. 2025 Aug 5;25(16):3921-3961. doi: 10.1039/d5lc00055f. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 40686367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microinjection molded microwell array-based portable digital PCR system for the detection of infectious respiratory viruses.Nano Converg. 2025 Mar 21;12(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40580-025-00482-5. Nano Converg. 2025. PMID: 40119017 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Step Detection of microRNA via the Programmable DNAzyme Probe-Mediated Multiple Signal Recycling.ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 25;10(13):13715-13721. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01877. eCollection 2025 Apr 8. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40224408 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

