A blood-based multi-pathway biomarker assay for early detection and staging of Alzheimer's disease across ethnic groups
- PMID: 38183344
- PMCID: PMC10984431
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13676
A blood-based multi-pathway biomarker assay for early detection and staging of Alzheimer's disease across ethnic groups
Abstract
Introduction: Existing blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease (AD) mainly focus on its pathological features. However, studies on blood-based biomarkers associated with other biological processes for a comprehensive evaluation of AD status are limited.
Methods: We developed a blood-based, multiplex biomarker assay for AD that measures the levels of 21 proteins involved in multiple biological pathways. We evaluated the assay's performance for classifying AD and indicating AD-related endophenotypes in three independent cohorts from Chinese or European-descent populations.
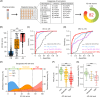
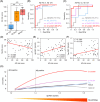
Results: The 21-protein assay accurately classified AD (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUC] = 0.9407 to 0.9867) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI; AUC = 0.8434 to 0.8945) while also indicating brain amyloid pathology. Moreover, the assay simultaneously evaluated the changes of five biological processes in individuals and revealed the ethnic-specific dysregulations of biological processes upon AD progression.
Discussion: This study demonstrated the utility of a blood-based, multi-pathway biomarker assay for early screening and staging of AD, providing insights for patient stratification and precision medicine.
Highlights: The authors developed a blood-based biomarker assay for Alzheimer's disease. The 21-protein assay classifies AD/MCI and indicates brain amyloid pathology. The 21-protein assay can simultaneously assess activities of five biological processes. Ethnic-specific dysregulations of biological processes in AD were revealed.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid pathology; blood biomarkers; disease staging; early detection; patient stratification; precision medicine.
© 2024 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Yuanbing Jiang, Fanny C. Ip, Amy K. Y. Fu, and Nancy Y. Ip are inventors of the related technology licensed to Cognitact. Yuanbing Jiang and Fanny C. Ip are co‐founders, and Li Ouyang is a current staff member of Cognitact. John Hardy has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly and Eisai. Albert Puig‐Pijoan has served on advisory boards for Schwabe Farma Ibérica. Marc Suárez‐Calvet has served as a consultant and on advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. and has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Roche Diagnostics, S.L.U. and Roche Farma, S.A. Henrik Zetterberg has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for AbbVie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, NervGen, Novo Nordisk, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, AlzeCure, Biogen, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside of the submitted work). All other authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information S2.
Figures



References
-
- Van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:9‐21. - PubMed
-
- Mintun MA, Lo AC, Duggan Evans C, et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1691‐1704. - PubMed
-
- Karikari TK, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:422‐433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFE0203000/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- C6027-19GF/Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (Collaborative Research Fund)
- T13-605/18 W/Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (Theme-Based Research Scheme)
- CTFCF18SC01/Chow Tai Fook Charity Foundation
- 2018B030336001/Guangdong Provincial Key S&T Program
- 2019B1515130004/Guangdong Provincial Fund for Basic and Applied Basic Research
- 2021Szvup137/Fundamental Research Program of Shenzhen Virtual University Park
- AoE/M-604/16/Areas of Excellence Scheme of the University Grants Committee
- ITCPD/17-9/Innovation and Technology Commission (InnoHK)
- INNOHK18SC01/Innovation and Technology Commission (InnoHK)
- ITS/207/18FP/Innovation and Technology Commission (InnoHK)
- MRP/042/18X/Innovation and Technology Commission (InnoHK)
- MRP/097/20X/Innovation and Technology Commission (InnoHK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

