Azilsartan Attenuates 3-Nitropropinoic Acid-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: The Role of IĸB/NF-ĸB and KEAP1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 38184805
- PMCID: PMC10901959
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-023-04083-8
Azilsartan Attenuates 3-Nitropropinoic Acid-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: The Role of IĸB/NF-ĸB and KEAP1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
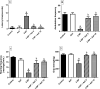
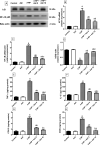
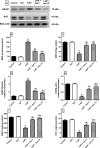
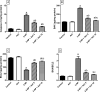
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal-dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor, psychiatric and cognitive symptoms. Injection of 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) is a widely used experimental model for induction of HD. The current study aimed to inspect the potential neuroprotective properties of azilsartan (Azil), an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker (ATR1), in 3-NP-induced striatal neurotoxicity in rats. Rats were randomly allocated into five groups and treated for 14 days as follows: group I received normal saline; group II received Azil (10 mg/kg, p.o.); group III received 3-NP (10 mg/kg, i.p); group IV and V received Azil (5 or 10 mg/kg, p.o, respectively) 1 h prior to 3-NP injection. Both doses of Azil markedly attenuated motor and behavioural dysfunction as well as striatal histopathological alterations caused by 3-NP. In addition, Azil balanced striatal neurotransmitters levels as evidenced by the increase of striatal gamma-aminobutyric acid content and the decrease of glutamate content. Azil also amended neuroinflammation and oxidative stress via modulating IĸB/NF-ĸB and KEAP1/Nrf2 downstream signalling pathways, as well as reducing iNOS and COX2 levels. Moreover, Azil demonstrated an anti-apoptotic activity by reducing caspase-3 level and BAX/BCL2 ratio. In conclusion, the present study reveals the neuroprotective potential of Azil in 3-NP-induced behavioural, histopathological and biochemical changes in rats. These findings might be attributed to inhibition of ATR1/NF-κB signalling, modulation of Nrf2/KEAP1 signalling, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic properties.
Keywords: 3-nitropropionic acid; Azilsartan; Huntington’s disease; NF-ĸB; Nrf2; Rat.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by tropisetron mitigates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease in rats: Role of PI3K/Akt and JAK2/NF-κB signaling pathways.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Apr 25;393:110957. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110957. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38513929
-
Sulforaphane Ameliorates 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Toxicity by Activating the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway and Inhibiting the MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2619-35. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9230-2. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26096705
-
Harmine prevents 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats via enhancing NRF2-mediated signaling: Involvement of p21 and AMPK.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;927:175046. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175046. Epub 2022 May 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35623405
-
Divulging the Intricacies of Crosstalk Between NF-Kb and Nrf2-Keap1 Pathway in Neurological Complications of COVID-19.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;58(7):3347-3361. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02344-7. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33683626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic insights on the role of Nrf-2 signalling in Huntington's disease.Neurol Sci. 2025 Feb;46(2):593-604. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07802-3. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39392523 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Defenses in Huntington's Disease: Roles of NRF2 and PGC-1α, and Therapeutic Strategies.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;15(4):577. doi: 10.3390/life15040577. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 3;25(7):3995. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073995. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612804 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

