Untargeted and temporal analysis of retinal lipidome in bacterial endophthalmitis
- PMID: 38185280
- PMCID: PMC10939753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2023.106806
Untargeted and temporal analysis of retinal lipidome in bacterial endophthalmitis
Abstract
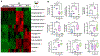
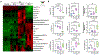
Bacterial endophthalmitis is a blinding infectious disease typically acquired during ocular surgery. We previously reported significant alterations in retinal metabolism during Staphylococcus (S) aureus endophthalmitis. However, the changes in retinal lipid composition during endophthalmitis are unknown. Here, using a mouse model of S. aureus endophthalmitis and an untargeted lipidomic approach, we comprehensively analyzed temporal alterations in total lipids and oxylipin in retina. Our data showed a time-dependent increase in the levels of lipid classes, sphingolipids, glycerolipids, sterols, and non-esterified fatty acids, whereas levels of phospholipids decreased. Among lipid subclasses, phosphatidylcholine decreased over time. The oxylipin analysis revealed increased prostaglandin-E2, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, and α-linolenic acid. In-vitro studies using mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages showed increased lipid droplets and lipid-peroxide formation in response to S. aureus infection. Collectively, these findings suggest that S. aureus-infection alters the retinal lipid profile, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of bacterial endophthalmitis.
Keywords: Endophthalmitis; Inflammation; Lipidomic; Oxylipins; Retina; S. aureus.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
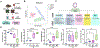

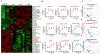

Similar articles
-
Role of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factors in Inducing Inflammation and Vascular Permeability in a Mouse Model of Bacterial Endophthalmitis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0128423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128423. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26053426 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal retinal transcriptome and systems biology analysis identifies key pathways and hub genes in Staphylococcus aureus endophthalmitis.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 11;6:21502. doi: 10.1038/srep21502. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26865111 Free PMC article.
-
Functional lipid diversity and novel oxylipin identification for interspecies differentiation and nutritional assessment of commercial seahorse (Hippocampus) using untargeted and targeted lipidomics.Food Chem. 2025 May 1;473:143117. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143117. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39892350
-
Accessory gene regulator controls Staphylococcus aureus virulence in endophthalmitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 Aug;36(9):1828-36. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995. PMID: 7635657
-
Staphylococcus aureus and its Bearing on Ophthalmic Disease.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2017 Feb;25(1):111-121. doi: 10.3109/09273948.2015.1075559. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 26679534 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic profiling reveals immunomodulatory role of IL-33 in ocular bacterial and fungal infections.Infect Immun. 2025 Jul 8;93(7):e0018325. doi: 10.1128/iai.00183-25. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 40512033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burton MJ, Ramke J, Marques AP, Bourne RRA, Congdon N, Jones I, Ah Tong BAM, Arunga S, Bachani D, Bascaran C, Bastawrous A, Blanchet K, Braithwaite T, Buchan JC, Cairns J, Cama A, Chagunda M, Chuluunkhuu C, Cooper A, Crofts-Lawrence J, Dean WH, Denniston AK, Ehrlich JR, Emerson PM, Evans JR, Frick KD, Friedman DS, Furtado JM, Gichangi MM, Gichuhi S, Gilbert SS, Gurung R, Habtamu E, Holland P, Jonas JB, Keane PA, Keay L, Khanna RC, Khaw PT, Kuper H, Kyari F, Lansingh VC, Mactaggart I, Mafwiri MM, Mathenge W, McCormick I, Morjaria P, Mowatt L, Muirhead D, Murthy GVS, Mwangi N, Patel DB, Peto T, Qureshi BM, Salomao SR, Sarah V, Shilio BR, Solomon AW, Swenor BK, Taylor HR, Wang N, Webson A, West SK, Wong TY, Wormald R, Yasmin S, Yusufu M, Silva JC, Resnikoff S, Ravilla T, Gilbert CE, Foster A, Faal HB, The Lancet Global Health Commission on Global Eye Health: vision beyond 2020, Lancet Glob Health 9(4) (2021) e489–e551. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

