Metabolic regulation of tumor-associated macrophage heterogeneity: insights into the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 38185636
- PMCID: PMC10773124
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-023-00549-7
Metabolic regulation of tumor-associated macrophage heterogeneity: insights into the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapeutic opportunities
Abstract
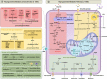
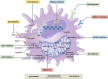
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are a heterogeneous population that play diverse functions in tumors. Their identity is determined not only by intrinsic factors, such as origins and transcription factors, but also by external signals from the tumor microenvironment (TME), such as inflammatory signals and metabolic reprogramming. Metabolic reprogramming has rendered TAM to exhibit a spectrum of activities ranging from pro-tumorigenic to anti-tumorigenic, closely associated with tumor progression and clinical prognosis. This review implicates the diversity of TAM phenotypes and functions, how this heterogeneity has been re-evaluated with the advent of single-cell technologies, and the impact of TME metabolic reprogramming on TAMs. We also review current therapies targeting TAM metabolism and offer new insights for TAM-dependent anti-tumor immunotherapy by focusing on the critical role of different metabolic programs in TAMs.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Metabolic reprogramming; Single-cell omics; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Manipulation of the tumor immuno-microenvironment via TAM-targeted expression of transcription factors.Immunol Res. 2022 Aug;70(4):432-440. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09277-w. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35486115 Review.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages employ immunoediting mechanisms in colorectal tumor progression: Current research in Macrophage repolarization immunotherapy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Mar;116:109569. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109569. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36773572 Review.
-
The Interface of Tumour-Associated Macrophages with Dying Cancer Cells in Immuno-Oncology.Cells. 2022 Dec 2;11(23):3890. doi: 10.3390/cells11233890. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of macrophage in regulating tumour microenvironment and the strategies for reprogramming tumour-associated macrophages in antitumour therapy.Eur J Cell Biol. 2021 Mar;100(2):151153. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151153. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33476912 Review.
-
Metabolic reprograming of tumor-associated macrophages.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Aug;8(16):1030. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2037. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32953830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
APOE-high myeloid cells are uniquely associated with metastatic intrathoracic lymph nodes obtained by EBUS-TBNA in primary lung cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Aug 20;9(1):292. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-01091-5. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40835684 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages at the Crossroads of Chronic Stress and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6838. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146838. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells; mechanisms, functional significance, and targeting in cancer therapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025 Jun;48(3):559-590. doi: 10.1007/s13402-025-01051-y. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025. PMID: 39998754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The next frontier in immunotherapy: potential and challenges of CAR-macrophages.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;13(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00549-9. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39103972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-based Radiopharmaceuticals that target fibroblast activation protein alpha: a review of current progress.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025 Jun 21;10(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s41181-025-00356-5. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025. PMID: 40542914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 81930064/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930064/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930064/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930064/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930064/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022YFC2704200/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 2022YFC2704200/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 22XD1402000/the Program of Shanghai Academic/ Technology Research Leader
- 22XD1402000/the Program of Shanghai Academic/ Technology Research Leader
- 22XD1402000/the Program of Shanghai Academic/ Technology Research Leader
- 22XD1402000/the Program of Shanghai Academic/ Technology Research Leader
- 22XD1402000/the Program of Shanghai Academic/ Technology Research Leader
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

