Gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor presented with severe anemia and inflammation: a case report
- PMID: 38185719
- PMCID: PMC10772034
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-023-01802-9
Gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor presented with severe anemia and inflammation: a case report
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare stromal tumor, often found in children and young adults, and most commonly occurs in the lungs. Surgical resection is considered the standard treatment for localized IMT, although only limited data exist. Gastric IMT in adults is extremely rare, and there are no established guidelines for its treatment.
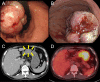
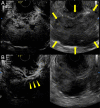
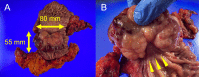
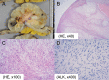
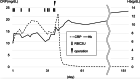
Case presentation: A 69-year-old male presented with persistent fatigue and weakness. Laboratory examination revealed severe anemia and inflammation. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy at admission revealed a 40-mm type I softish tumor in the lesser curvature of the gastric body, without apparent hemorrhage. Repeated biopsies, including partial resection with snare, failed to give a definitive diagnosis. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a massive lesion at the gastric body, protruding into the gastric lumen, which was consistent with the gastric tumor. After admission, the patient developed anemia refractory to frequent blood transfusions despite the absence of apparent gastrointestinal bleeding. In addition, the patient had recurrent fevers of 38 °C or higher, and persistent high inflammatory levels. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) CT 1 month after the first visit exhibited an increased FDG uptake in the gastric tumor. In addition, this CT scan revealed a rapid increase in tumor size to 75 mm. It was suspected that the undiagnosed gastric tumor caused these serious clinical symptoms, and he underwent distal gastrectomy and cholecystectomy. The gross image of the tumor showed an 80-mm cauliflower-like shape with a gelatinous texture. The histopathological diagnosis was IMT. The postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient's symptoms subsided drastically, improving both anemia and systemic inflammation. The patient has shown no recurrence or relapse of the symptoms over one and a half years.
Conclusions: In this case, the tumor resection finally enabled the diagnosis of IMT and resolved the clinical symptoms. Despite its predominantly benign morphological nature, some cases of IMT present clinically adverse courses. Surgical treatment may lead to its final diagnosis and improvement of clinical symptoms.
Keywords: Anemia; Gut; Inflammation; Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor; Surgery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Gastric and cardiac inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: an extremely rare case.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Jan 29;19(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02481-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38287440 Free PMC article.
-
Rare gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in an adult woman: a case report with review of the literature.Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:374070. doi: 10.1155/2012/374070. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Case Rep Med. 2012. PMID: 22570660 Free PMC article.
-
Melena as presentation of primary small intestine inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in an adult woman. A case report.Ann Ital Chir. 2015 Jul 29;86(ePub):S2239253X15024032. Ann Ital Chir. 2015. PMID: 26240947 Review.
-
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in children: diagnosis and treatment.J Pediatr Surg. 2001 Jun;36(6):908-12. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2001.23970. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. PMID: 11381424 Review.
References
-
- Lovly CM, Gupta A, Lipson D, Otto G, Brennan T, Chung CT, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors harbor multiple potentially actionable kinase fusions. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:889–895. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0377. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

