Targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): from bench to bedside
- PMID: 38185721
- PMCID: PMC10772138
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01690-3
Targeting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): from bench to bedside
Abstract
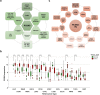
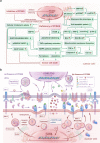
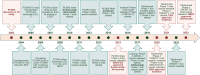
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) has evolved as a pivotal enzyme in lipid metabolism and a revolutionary therapeutic target for hypercholesterolemia and its related cardiovascular diseases (CVD). This comprehensive review delineates the intricate roles and wide-ranging implications of PCSK9, extending beyond CVD to emphasize its significance in diverse physiological and pathological states, including liver diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and notably, cancer. Our exploration offers insights into the interaction between PCSK9 and low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLRs), elucidating its substantial impact on cholesterol homeostasis and cardiovascular health. It also details the evolution of PCSK9-targeted therapies, translating foundational bench discoveries into bedside applications for optimized patient care. The advent and clinical approval of innovative PCSK9 inhibitory therapies (PCSK9-iTs), including three monoclonal antibodies (Evolocumab, Alirocumab, and Tafolecimab) and one small interfering RNA (siRNA, Inclisiran), have marked a significant breakthrough in cardiovascular medicine. These therapies have demonstrated unparalleled efficacy in mitigating hypercholesterolemia, reducing cardiovascular risks, and have showcased profound value in clinical applications, offering novel therapeutic avenues and a promising future in personalized medicine for cardiovascular disorders. Furthermore, emerging research, inclusive of our findings, unveils PCSK9's potential role as a pivotal indicator for cancer prognosis and its prospective application as a transformative target for cancer treatment. This review also highlights PCSK9's aberrant expression in various cancer forms, its association with cancer prognosis, and its crucial roles in carcinogenesis and cancer immunity. In conclusion, this synthesized review integrates existing knowledge and novel insights on PCSK9, providing a holistic perspective on its transformative impact in reshaping therapeutic paradigms across various disorders. It emphasizes the clinical value and effect of PCSK9-iT, underscoring its potential in advancing the landscape of biomedical research and its capabilities in heralding new eras in personalized medicine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

