Giant Villous Adenoma of the Rectum With Prolapse: Case Report
- PMID: 38186509
- PMCID: PMC10770438
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50079
Giant Villous Adenoma of the Rectum With Prolapse: Case Report
Abstract
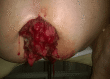
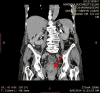
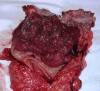
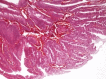
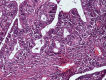
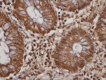
Colorectal polyps, frequently adenomas, are common in older adults, with villous adenomas being a notable subset due to their potential for significant malignancy risk. This case report highlights a rare instance of a giant villous adenoma in a 79-year-old female patient, challenging in both diagnosis and treatment. The patient, with a history of untreated essential arterial hypertension, was hospitalized for severe anemia following a massive rectal hemorrhage. An irreducible, prolapsed rectal mass was evident upon examination, and further investigations, including rectoscopy and abdominopelvic computed tomography scan, confirmed a villous adenoma with severe dysplasia. Given the tumor's substantial size, circumferential nature, and proximity to the dentate line, an abdominoperineal resection using the Miles technique was performed. The histopathological examination post-surgery confirmed the presence of a villous adenoma with high-grade epithelial neoplasia and localized areas of well-differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma. This case underscores the diagnostic and management complexities of large villous adenomas, emphasizing the need for meticulous surgical decision-making to ensure oncological safety and patient welfare, particularly when conservative resection may be inadequate.
Keywords: emergency gastroenterology and endoscopy; giant villous adenoma; inferior digestive hemorrhage; proctology; villous tumor.
Copyright © 2023, Munteanu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Clinical significance of small polyps found during screening with flexible sigmoidoscopy. Farraye FA, Wallace M. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2002;12:41–51. - PubMed
-
- [A new one in the classification of benign colon epithelial tumors (WHO, 2019, 5th edition)] Oleynikova NA, Malkov PG, Danilova NV. Arkh Patol. 2020;82:35–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
