D-dimer as a Rule-Out for Aortic Dissection
- PMID: 38186548
- PMCID: PMC10771797
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50170
D-dimer as a Rule-Out for Aortic Dissection
Abstract
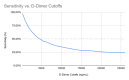
Introduction Acute aortic dissection (AAD) represents a significant diagnostic challenge with a high mortality rate if not treated promptly. This challenge arises from the diverse clinical presentations of AAD, and its symptom overlap with other medical conditions. Although both helical CT and transesophageal echocardiography are reliable diagnostic tools for AAD, they are not feasible for every suspected case. Furthermore, limited research on D-dimer's utility in ruling out AAD has been conducted due to the condition's rarity. Methods This study utilizes the TriNetX database (https://trinetx.com/), encompassing data from 54 healthcare organizations across the United States over the past two decades from 85 million patients. The objective is to evaluate the sensitivity of an elevated D-dimer level in diagnosing AAD across a much larger patient cohort than previously studied. Results Retrospectively analyzing this dataset, there were 1,319 patients identified with a confirmed AAD who had undergone D-dimer testing within a day of diagnosis. Of these, 1,252 patients exhibited D-dimer levels exceeding 400 ng/ml while 1,227 had levels surpassing 500 ng/ml. Notably, a D-dimer cutoff of 400 ng/ml demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.949 while a 500 ng/ml cutoff yielded a sensitivity of 0.930. Conclusion This large retrospective cohort study demonstrates that a blood D-dimer level is highly sensitive in assaying for AAD. The D-dimer levels analyzed showed a remarkable sensitivity in ruling out AAD, avoiding the need for more invasive testing in low-risk patients.
Keywords: acute aortic dissection; cardiovascular; d-dimer; dissection of thoracic aorta; emergency medicine.
Copyright © 2023, Carter et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures
References
-
- Acute aortic dissection: population-based incidence compared with degenerative aortic aneurysm rupture. Clouse WD, Hallett JW Jr, Schaff HV, Spittell PC, Rowland CM, Ilstrup DM, Melton LJ 3rd. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004;79:176–180. - PubMed
-
- Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: a review of 505 cases. Hirst AE Jr, Johns VJ Jr, Kime SW Jr. https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/citation/1958/09000/dissecting_aneur.... Medicine (Baltimore) 1958;37:217. - PubMed
-
- The death of King George II, with a biographical note on Dr Frank Nicholls, physician to the King. Ross JK. J Med Biogr. 1999;7:228–233. - PubMed
-
- Insights from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection: a 20-year experience of collaborative clinical research. Evangelista A, Isselbacher EM, Bossone E, et al. Circulation. 2018;137:1846–1860. - PubMed
-
- Presentation, diagnosis, and outcomes of acute aortic dissection: 17-year trends from the international registry of acute aortic dissection. Pape LA, Awais M, Woznicki EM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:350–358. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous