Naked-eye detection with loop-mediated isothermal amplification for P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in agricultural products
- PMID: 38186613
- PMCID: PMC10766909
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-023-01315-z
Naked-eye detection with loop-mediated isothermal amplification for P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in agricultural products
Abstract
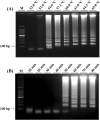
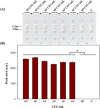
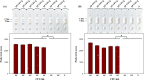
Pectobacterium carotovorum causing soft-rot disease requires on-site detection before the distribution of agricultural products. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), which is resistant to food inhibitors, is known for its high detection sensitivity for pathogens and when coupled with lateral flow immunoassay (LFA) enables visualizations. For detection of soft-rot disease, we developed a LAMP-LFA system targeting 16S ribosomal RNA, a partial sequence gene of P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. The LAMP-LFA was performed at 60 °C for 50 min followed by hybridization of digoxygenin-labeled LAMP amplicon and biotinylated probe. Detection sensitivity was 3.22 × 101 CFU/mL in pure culture, which specifically detected the target. In Chinese cabbage and potato, the target was detected up to low levels of 1.57 × 102 CFU/g and 1.29 × 102 CFU/g, respectively. This study showed potential applicability as a sensitive point-of-care system for soft-rot disease bacteria detection in agricultural products.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10068-023-01315-z.
Keywords: Agricultural product; Lateral flow immunoassay; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; Pectobacterium carotovorum; Soft-rot disease; Visualization detection.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
First Report of Bacterial Soft Rot of Potato Caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in Guangdong Province of China.Plant Dis. 2012 Dec;96(12):1819. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-07-12-0620-PDN. Plant Dis. 2012. PMID: 30727277
-
Development of a Bacteriophage Cocktail against Pectobacterium carotovorum Subsp. carotovorum and Its Effects on Pectobacterium Virulence.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Oct 11;88(19):e0076122. doi: 10.1128/aem.00761-22. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36165651 Free PMC article.
-
Specific detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum by loop-mediated isothermal amplification.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Dec;17(9):1499-1505. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12378. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26833881 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of Cabbage Soft Rot Caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in Malaysia.Plant Dis. 2011 Apr;95(4):491. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-10-0683. Plant Dis. 2011. PMID: 30743350
-
Characteristics and Rapid Diagnosis of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. Associated With Bacterial Soft Rot of Vegetables in China.Plant Dis. 2020 Apr;104(4):1158-1166. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-19-1033-RE. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Plant Dis. 2020. PMID: 32053476
References
-
- Adeolu M, Alnajar S, Naushad S, Gupta RS. Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 2016;66:5575–5599. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001485. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Charkowski AO. The soft rot Erwinia Plant-associated bacteria. Berlin: Springer; 2007. pp. 423–505.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
