Influence of physical education on anxiety, depression, and self-esteem among college students
- PMID: 38186731
- PMCID: PMC10768485
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i12.1121
Influence of physical education on anxiety, depression, and self-esteem among college students
Abstract
Background: Physical education is pivotal in our country's education reform. Urban schools have notably enhanced the intensity of physical education in recent years. However, the effects of physical education on students' anxiety, depression, and self-esteem levels, as well as their interrelations, remain unexplored.
Aim: To analyze the influence of physical education on students' anxiety, depression, and self-esteem.
Methods: This study employed a cross-sectional design. A stratified cluster sampling method was used to select 478 first-year university students. Self-administered questionnaires were used to investigate the physical education status and basic information of college students. We used the Physical Activity Rank Scale-3 (PARS-3), Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), and Self-Esteem Scale (SES) to assess the level of exercise, anxiety, depression, and self-esteem. Multiple Logistic regression was used to analyze the factors influencing anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve (AUC) were used to evaluate the predictive ability of PARS-3 scores for anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Spearman's correlation was used to analyze the correlations among the PARS-3, SAS, SDS, and SES.
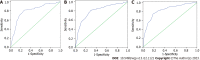
Results: Compared with the domestic norms, SAS and SDS scores were higher, and SES scores were lower (P < 0.05). Among the participants, 210 (43.93%) had PARS-3 scores below 20, 94 (19.67%) had scores of 20-42, and 174 (36.40%) had scores above 42. After adjusting for daily sleep time, gender, being an only child, major, father's educational background, mother's educational background, and family residence, PARS-3 scores were independent influencing factors for anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem (P < 0.05). The AUC of PARS-3 scores predicting anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem were 0.805 (0.760-0.849), 0.799 (0.755-0.843), and 0.831 (0.788-0.874), respectively. The sensitivities were 0.799, 0.801, and 0.748, and the specificities were 0.743, 0.716, and 0.814, respectively. PARS-3 was negatively correlated with SAS and SDS scores (r = -0.566, -0.621, both P < 0.001) and positively correlated with SES scores (r = -0.621, P < 0.001). SES scores were negatively correlated with SAS and SDS scores (r = -0.508, r = -0.518, both P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The amount of physical activity is negatively correlated with anxiety and depression degree and positively correlated with self-esteem degree.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Influence; Physical education; Self-esteem; Student.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of students with left-behind experiences on childhood: The relationship between negative life events and depression among college students in China.Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2018 Feb;64(1):56-62. doi: 10.1177/0020764017739332. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29145763
-
The influence of physical activity on internet addiction among Chinese college students: the mediating role of self-esteem and the moderating role of gender.BMC Public Health. 2024 Apr 1;24(1):935. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18474-1. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38561700 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of physical activity on depression in university students: the mediating role of self-esteem and positive psychological capital.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1485641. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1485641. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39380753 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Physical Exercise and Negative Emotions in College Students in the Post-Epidemic Era: The Mediating Role of Emotion Regulation Self-Efficacy.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 26;19(19):12166. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912166. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231469 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional historical study on the changes in self-esteem among Chinese adolescents from 1996 to 2019.Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1280041. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1280041. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38106402 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The mediating role of sleep quality on the relationship between physical activity and social anxiety disorder among Chinese college freshmen.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1599041. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1599041. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40735178 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesiophobia and its associated factors among patients after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a cross-sectional study based on latent profile analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04934-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40615953 Free PMC article.
-
Connection between college students' sports activities, depression, and anxiety: the mediating role of self-esteem.BMC Psychol. 2025 May 13;13(1):499. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02838-2. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40361214 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of physical exercise on mental health among female college students: the chain mediating role of coping styles and psychological resilience.Front Psychol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1466327. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1466327. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39624372 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Football Participation and Sport Trait Confidence for Adolescents: A Chain-Mediated Effect of Collective Self-Esteem and Self-Esteem.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;14(8):656. doi: 10.3390/bs14080656. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang X, Gao L, Yang J, Zhao F, Wang P. Parental Phubbing and Adolescents' Depressive Symptoms: Self-Esteem and Perceived Social Support as Moderators. J Youth Adolesc. 2020;49:427–437. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

