Management of COVID-19 during the second wave at a tertiary care public hospital in Eastern India: An experience from the administrative control room
- PMID: 38186772
- PMCID: PMC10771191
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1444_21
Management of COVID-19 during the second wave at a tertiary care public hospital in Eastern India: An experience from the administrative control room
Abstract
Context: Though many arrangements had been made during the first wave, multiple complaints were reported regarding the arrangements made for COVID patients. The control room was set up as a 24 × 7 administrative coordination center to attend to issues after the initial setup of COVID units.
Aim: To identify the major problems reported to the control room during the second wave of COVID-19 and find the related cause for the same.
Methods and materials: Issues reported to the control room were recorded from April to June (2021). The control room residents were asked to allocate each problem into six categories. Next, the residents allotted a frequency score to each of the problems depending on how regularly it was reported. Secondary data from various reports were also considered.
Statistical analysis used: Data were analyzed using MS Excel software.
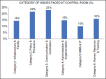
Results: Various administrative issues were identified to be due to issues in communication and coordination (23%), policy and procedures (22%), human resource and training (16%), administration and implementation (15%), infrastructure (14%), and HMIS and IT (10%).
Conclusion: Most frequent problems reported to the control room were related to infrastructure, policy implementation, and manpower training. After the initial implementation of new processes, there was a requirement for regular follow-up and coordination. This model of setting up an administrative control room and evidence-based approach will serve as a template for public hospitals to ensure coordination of hospital operations.
Keywords: COVID-19; Control room; hospital administration; hospital management; pandemic preparedness; second wave.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services . S.l.: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017. Pandemic Influenza Plan.
-
- Shukla D, Pradhan A, Malik P. Economic impact of COVID-19 on the Indian healthcare sector: An overview. Int J Comm Med Public Health. 2020;8:489–94.
-
- Kausar M, Ranjan R, Singh AR, Siddharth V, Sharma DK. Hospital administration control room: An effective concept for managing hospital operation issues: A study in tertiary care public sector hospital. Int J Res Foundation Hosp Healthc Adm. 2018;6:82–90.
-
- Baggs JG, Schmitt MH, Mushlin AI, Mitchell PH, Eldrege DH, Oakes D. Association between nurse-physician collaboration and patient outcomes in three intensive care units. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1991–8. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Geneva Switzerland: 2009. Pandemic Influenza Preparedness and Response: A WHO Guidance Document. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
