Funding of research & innovation in the field of medical technologies and biomedical engineering over the different European framework programmes
- PMID: 38186948
- PMCID: PMC10769974
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-023-00320-9
Funding of research & innovation in the field of medical technologies and biomedical engineering over the different European framework programmes
Abstract
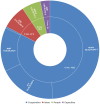
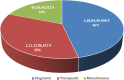
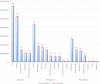
To demonstrate the role of the European Framework Programmes for Research & Innovation in supporting the field of Medical Technologies and Biomedical Engineering and to show which types of medical technologies and which funding instruments are the preferred ones. Based on data available in the European Commission data warehouse for the past two Framework Programmes, funded projects addressing a Medical Technology were identified. This enabled to categorize the projects according to the intended use and to classify into different types. Moreover, the main instruments in the Framework Programme acting as funding sources were explored. The increase in R&I support led to 1961 projects and a total financing of € 3.2 bllion under the last Framework Programme. The categorization showed a balanced funding in terms of intended use, the detailed classification revealed that in-vitro-diagnostics and imaging equipment prevail in the diagnostic category, tissue-engineering products, implants and robotics in the therapeutic domain and ICT or software-based technologies in the miscellaneous category. As to funding sources, the classical health-oriented collaborative research scheme was on top, followed by instruments like the European Research Council, the Future and Emerging Technologies activities and the European Innovation Council, and completed by the Public-Private Partnerships. The European Framework Programmes are key on the global landscape for financing Research & Innovation of Medical Technology and the breadth of supported technologies is equally reflected by the different funding instruments involved.
Keywords: Biomedical engineering; EU Framework programme; Funding; In-vitro-diagnostic; Medical device; Medical technology.
© Korean Society of Medical and Biological Engineering 2023, corrected publication 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe author declares that the work for this manuscript was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- MedTech Europe: innovation in medical technologies. Reflection Paper. 2020: https://www.medtecheurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/2020_mte_innova... Accessed 23 May 2023.
-
- European commission, community research and development information service CORDIS. Research programme (EEC) in the field of medical and public health research, consisting of three concerted projects, 1978–1981. 2014. https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/PRE_FWP_MHR-1C Accessed 26 May 2023
-
- European commission, community research and development information service CORDIS. Second research programme (EEC) in the field of medical and public health research, consisting of four multiannual concerted actions, 1980–1984. 2014. https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/PRE_FWP_MHR-2C. Accessed 26 May 2023
-
- European commission, community research and development information service CORDIS. Sectoral research and development programme (EEC) in the field of medical and public health research - concerted action, 1982–1986. 2014. https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/PRE_FWP_MHR-3C Accessed 26 May 2023
-
- European commission, community research and development information service CORDIS. Research and development coordination programme (EEC) in the field of medical and health research, 1987–1991. 2014. https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/FP2-MHR-4C Accessed 26 May 2023
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
