Molecular mechanism of Shengyang Yiwei Decoction in treating chronic kidney disease based on network pharmacology
- PMID: 38186988
- PMCID: PMC10767527
Molecular mechanism of Shengyang Yiwei Decoction in treating chronic kidney disease based on network pharmacology
Abstract
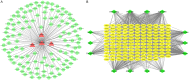
There is a serious worldwide health problem caused by chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet there are few viable therapies. Therapeutic promise in the treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been shown by the use of the traditional Chinese herbal compound Shengyang Yiwei Decoction (SYD). However, the chemical processes through which SYD exerts its effects are still unknown. The purpose of this network pharmacology research is to better understand the molecular mechanism of action of Shengyang Yiwei Decoction (SYD) in the treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP) was first searched for information on the chemical components of Shengyang Yiwei Decoction. The molecular targets of SYD were then predicted using the Pharm Mapper service. After that, we used databases like DIG-SEE, TTD, and OMIM to zero down on the targets most closely linked to CKD. Cytoscape 3.2.1 was used to generate the component-target network representing SYD's therapy of CKD. In addition, KEGG signal pathways and GO biological processes were analyzed using the DAVID database, and the findings were displayed via OmicShare Tools. Twenty-two active components were isolated from Shengyang Yiwei Decoction, and they were linked to 36 therapeutic targets for CKD in the current investigation. According to the results of the network pharmacology study, 41 signaling pathways are involved in mediating the therapeutic effects of SYD. In addition, SYD's broad therapeutic impact in CKD therapy was shown to include 29 molecular activities, 14 cell components, and 91 biological processes. This research utilizes a multivariate analysis to provide light on the strategies and outcomes of treating CKD using Shengyang Yiwei Decoction. Clinical therapeutic methods for CKD management may benefit greatly from a thorough knowledge of the underlying processes and material foundation of this disease.
Keywords: Protein-protein interaction network; Shengyang Yiwei Decoction; chronic kidney disease; miRNA-mRNA regulatory network.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism Study on the Regulation of Th1/Th2 in the Treatment of Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy by Shengyang Yiwei Decoction.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025 Jan 13. doi: 10.2174/0113862073322871241108065718. Online ahead of print. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 39812058
-
Clinical Efficacy of Modified Yiwei Shengyang Decoction Combined with FOLFOX4 Chemotherapy Regimen in the Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer and Its Effect on Tumor Marker Levels.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 5;2022:6234032. doi: 10.1155/2022/6234032. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9763612. doi: 10.1155/2023/9763612. PMID: 35571732 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Shengyang Yiwei Decoction for the treatment of chronic gastritis: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22869. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022869. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120827 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Chongcaoyishen Decoction Against Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 31;9:847812. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.847812. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35433831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the pharmacological mechanism of Astragaloside IV in alleviating urotensin II-mediated renal tubular epithelial cell injury.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 20;19(12):e0310210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310210. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39705287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laster ML, Rowan B, Chen HC, Schwantes-An TH, Sheng X, Friedman PA, Ikizler TA, Sinshiemer JS, Ix JH, Susztak K, de Boer IH, Kestenbaum B, Hung A, Moe SM, Perwad F, Robinson-Cohen C. Genetic variants associated with mineral metabolism traits in chronic kidney disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:e3866–e3876. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
