Bioactive components and the molecular mechanism of Shengxian Decoction against lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 38186989
- PMCID: PMC10767532
Bioactive components and the molecular mechanism of Shengxian Decoction against lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to identify the active components of Shengxian Decoction (SXT) and to elucidate the multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway regulatory mechanisms underlying the efficacy of SXT in treating lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
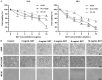
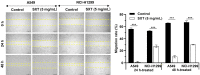
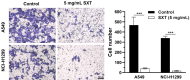
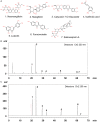
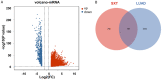
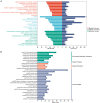
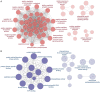
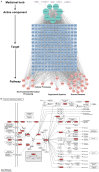
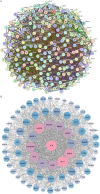
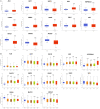
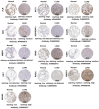
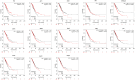
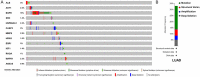
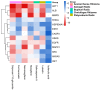
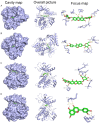
Methods: The effects of SXT extract on proliferation, migration, and invasion capabilities of human LUAD cells were determined through 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), wound healing, and Transwell assays. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) was employed to pinpoint the primary active constituents of SXT. The SXT-active component-target-pathway network and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were constructed based on network pharmacology. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed using DAVID. The clinical significance of key targets was assessed using several external databases, and molecular docking confirmed the binding affinities between key targets and SXT active components.
Results: SXT significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of human LUAD cells. HPLC identified and quantified seven active SXT components. Network pharmacology yielded 197 targets, 128 signaling pathways, and 448 GO terms. The PPI network and external validation underscored 13 key targets significantly associated with the influence of SXT on LUAD progression. Molecular docking demonstrated strong interactions between SXT active components and key targets.
Conclusion: SXT treats LUAD through a multifaceted approach involving various components, targets, and pathways. This research offers novel insights into the constituents and molecular mechanisms of SXT in LUAD therapy.
Keywords: Shengxian Decoction (SXT); active components; lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD); molecular docking; network pharmacology.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical and Biological Evidence of the Efficacy of Shengxian Decoction for Treating Human Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 18;12:849579. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.849579. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35372052 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of bufalin against lung adenocarcinoma: New and comprehensive evidences from network pharmacology, metabolomics and molecular biology experiment.Comput Biol Med. 2023 May;157:106777. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106777. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36924737
-
Exploration of the Mechanism of Shengxian Decoction Against Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2023 Aug-Sep;21(6):258-272. doi: 10.1089/adt.2023.006. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2023. PMID: 37682969
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based analyses to predict the potential mechanism of Huangqin decoction in treating colorectal cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jul 6;11(19):4553-4566. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4553. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37469733 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the SIRT3/SOD2 Signaling Pathway by a Compound Mixture from Polygonum orientale L. for Myocardial Damage.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;17(10):1288. doi: 10.3390/ph17101288. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
