Genetic estimation of correlations between circulating glutamine and cancer
- PMID: 38187059
- PMCID: PMC10767347
Genetic estimation of correlations between circulating glutamine and cancer
Abstract
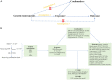
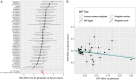
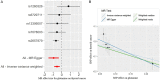
The controversy regarding the causal relationship between circulating glutamine and cancer risk remains unresolved. Here, we aim to assess the causal impact of glutamine on the risk of six prevalent cancer types and their respective subtypes including breast, lung, ovarian, thyroid, prostate, and endometrial cancers. A Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was conducted to evaluate the causal effect of circulating glutamine on cancers risk. Data on circulating glutamine were extracted from the UK Biobank (UKB), comprising 114,750 European patients. To ensure the validity of our findings, we employed several analytical approaches, such as inverse variance weighting, weighted median, weighted mode test, MR-Egger regression, and MR-PRESSO method. Both univariable and multivariable MR analyses were conducted. Additionally, we employed a large-scale summary-level study on circulating glutamine involving 24,925 European participants for validation purposes. Our MR analysis reveals a causal association between circulating glutamine and thyroid cancer in both the UKB cohort (IVW: OR = 0.667, 95% CI [0.541-0.822], P = 1.52×10-4) and the validated cohort (IVW: OR = 0.577, 95% CI [0.421-0.790], P = 6.14×10-4). Sensitivity analysis, including multivariable MR analyses, consistently supports this finding (P < 0.05), affirming the reliability and robustness of our study. Our findings indicate an inverse correlation between circulating glutamine and the incidence of thyroid cancer in European populations. However, further research encompassing diverse ancestries is necessary to validate this causal relationship.
Keywords: Circulating glutamine; GWAS; Mendelian randomization; UK Biobank; cancer; genetics.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Causal effects of circulating glutamine on colitis, IBD, and digestive system cancers: a Mendelian randomisation study.J Cancer. 2024 May 20;15(12):3738-3749. doi: 10.7150/jca.96085. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38911392 Free PMC article.
-
Association between circulating vitamin E and ten common cancers: evidence from large-scale Mendelian randomization analysis and a longitudinal cohort study.BMC Med. 2022 May 11;20(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02366-5. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 35538486 Free PMC article.
-
Causal association between telomere length and female reproductive endocrine diseases: a univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization analysis.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Jul 15;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01466-5. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 39010148 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Exploring the potential causal relationship between gut microbiota and heart failure: A two-sample mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Feb;49(2):102235. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102235. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38040216 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic prediction of patients having classical papillary thyroid carcinoma with a 4 mRNA-based risk model.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 7;103(23):e38472. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038472. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38847736 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effects of circulating glutamine on colitis, IBD, and digestive system cancers: a Mendelian randomisation study.J Cancer. 2024 May 20;15(12):3738-3749. doi: 10.7150/jca.96085. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38911392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu T, Han C, Fang P, Ma Z, Wang X, Chen H, Wang S, Meng F, Wang C, Zhang E, Dong G, Zhu H, Yin W, Wang J, Zuo X, Qiu M, Wang J, Qian X, Shen H, Xu L, Hu Z, Yin R. Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific lncRNA LINC01614 enhances glutamine uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:141. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
