Small RNA signatures of the anterior cruciate ligament from patients with knee joint osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38187089
- PMCID: PMC10768046
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1266088
Small RNA signatures of the anterior cruciate ligament from patients with knee joint osteoarthritis
Abstract
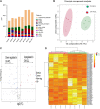
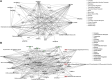
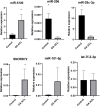
Introduction: The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is susceptible to degeneration, resulting in joint pain, reduced mobility, and osteoarthritis development. There is currently a paucity of knowledge on how anterior cruciate ligament degeneration and disease leads to osteoarthritis. Small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs), such as microRNAs and small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), have diverse roles, including regulation of gene expression. Methods: We profiled the sncRNAs of diseased osteoarthritic ACLs to provide novel insights into osteoarthritis development. Small RNA sequencing from the ACLs of non- or end-stage human osteoarthritic knee joints was performed. Significantly differentially expressed sncRNAs were defined, and bioinformatics analysis was undertaken. Results and Discussion: A total of 184 sncRNAs were differentially expressed: 68 small nucleolar RNAs, 26 small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and 90 microRNAs. We identified both novel and recognized (miR-206, -365, and -29b and -29c) osteoarthritis-related microRNAs and other sncRNAs (including SNORD72, SNORD113, and SNORD114). Significant pathway enrichment of differentially expressed miRNAs includes differentiation of the muscle, inflammation, proliferation of chondrocytes, and fibrosis. Putative mRNAs of the microRNA target genes were associated with the canonical pathways "hepatic fibrosis signaling" and "osteoarthritis." The establishing sncRNA signatures of ACL disease during osteoarthritis could serve as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets in ACL degeneration and osteoarthritis development.
Keywords: anterior cruciate ligament; microRNA; osteoarthritis; small nuclear RNA; small nucleolar RNA.
Copyright © 2023 Kharaz, Zamboulis, Fang, Welting, Peffers and Comerford.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer RG declared a shared parent affiliation with the author TW to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Small Non-Coding RNAome of Ageing Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 7;21(16):5675. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165675. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784773 Free PMC article.
-
Equine synovial fluid small non-coding RNA signatures in early osteoarthritis.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Jan 9;17(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02707-7. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33422071 Free PMC article.
-
Small non-coding RNA signatures in atrial appendages of patients with atrial fibrillation.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18483. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18483. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39051629 Free PMC article.
-
Small non-coding RNAs as important players, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in multiple sclerosis: A comprehensive overview.J Autoimmun. 2019 Jul;101:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 20. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 31014917 Review.
-
Prevalence of patellofemoral joint osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament injury and associated risk factors: A systematic review.J Orthop Translat. 2019 Aug 6;22:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.07.004. eCollection 2020 May. J Orthop Translat. 2019. PMID: 32440495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Non-Coding RNAome of Ageing Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 7;21(16):5675. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165675. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784773 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of small RNAs in inflammatory bowel disease and associated colorectal cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Feb;55(2):33. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5474. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39704210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma and synovial fluid extracellular vesicles display altered microRNA profiles in horses with naturally occurring post-traumatic osteoarthritis: an exploratory study.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024 Apr 13;262(S1):S83-S96. doi: 10.2460/javma.24.02.0102. Print 2024 Jun 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38593834 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

