Is the Blood Pressure-Enabled Smartwatch Ready to Drive Precision Medicine? Supporting Findings From a Validation Study
- PMID: 38187511
- PMCID: PMC10769613
- DOI: 10.14740/cr1569
Is the Blood Pressure-Enabled Smartwatch Ready to Drive Precision Medicine? Supporting Findings From a Validation Study
Abstract
Background: The popular wrist-worn wearables recording a variety of health metrics such as blood pressure (BP) in real time could play a potential role to advance precision medicine, but these devices are often insufficiently validated for their performance to enhance confidence in its use across diverse populations. The accuracy of BP-enabled smartwatch is assessed among the multi-ethnic Malaysians, and findings is discussed in comparison with conventional automated upper-arm BP device.
Methods: Validation procedures followed the guidelines by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation/European Society of Hypertension/International Organization for Standardization (AAMI/ESH/ISO) Universal Standard (ISO 81060-2:2018). Quota sampling was employed to obtain eligible patients with normal and abnormal BP as per guideline. The measurements of BP were taken at wrist using HUAWEI WATCH D (test BP); and the readings were assessed against reference BP by the mercury sphygmomanometer. Agreement statistics and linear regression analyses were performed.
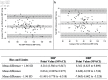
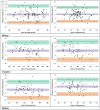
Results: BP measurements (234 data pairs) from 78 patients that fulfilled AAMI/ESH/ISO protocol were analyzed. The BP readings taken by the HUAWEI WATCH D were comparable to reference BP by sphygmomanometer based on 1) Criterion 1: systolic blood pressure (SBP) = -0.034 (SD 5.24) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) = -0.65 (SD 4.66) mm Hg; and 2) Criterion 2: SBPs = -0.034 (SD 4.18) and DBPs = -0.65 (SD 3.94) mm Hg. Factors of sociodemographic characteristics, anthropometric measurements, cardiovascular comorbidities, and wrist hair density were not significantly associated with the mean BP differences.
Conclusions: HUAWEI WATCH D fulfilled criteria 1 and 2 of the AAMI/ESH/ISO Universal Standard (ISO 81060-2:2018) guidelines. It can be recommended for clinical use across a wider population. The rich data from real-time BP measurements in concurrent with other health-related parameters recorded by the smartwatch wearable offer opportunities to drive precision medicine in tackling therapeutic inertia by personalizing BP control regimen.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Precision health; Precision medicine; Smartwatch; Validation; Wearables; mHealth.
Copyright 2023, Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LWL received funding from Huawei Technologies (Malaysia).
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel blood pressure monitoring technique by smart HUAWEI WATCH: A validation study according to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO 81060-2:2018 guidelines.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 11;9:923655. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.923655. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36304535 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the watch-type HUAWEI WATCH D oscillometric wrist blood pressure monitor in adult Chinese.Blood Press Monit. 2022 Oct 1;27(5):353-356. doi: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000608. Epub 2022 May 27. Blood Press Monit. 2022. PMID: 35687029
-
Accuracy of the Withings BPM Connect Device for Self-Blood Pressure Measurements in General Population - Validation According to the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation/European Society of Hypertension/International Organization for Standardization Universal Standard.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022 Mar 31;18:191-200. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S350006. eCollection 2022. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35386428 Free PMC article.
-
A Universal Standard for the Validation of Blood Pressure Measuring Devices: Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation/European Society of Hypertension/International Organization for Standardization (AAMI/ESH/ISO) Collaboration Statement.Hypertension. 2018 Mar;71(3):368-374. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10237. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 29386350 Review.
-
Improving the accuracy of blood pressure measurement: the influence of the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol (ESH-IP) for the validation of blood pressure measuring devices and future perspectives.J Hypertens. 2018 Mar;36(3):479-487. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001635. J Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29384984
Cited by
-
Validation of the DBP-8278B Wrist-type Fully Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor in the general population according to the ISO 81060-2:2018/AMD 1:2020 protocol.Blood Press Monit. 2025 Feb 1;30(1):36-39. doi: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000717. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Blood Press Monit. 2025. PMID: 39008688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- N. C. D. R. F. Collaboration. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398(10304):957–980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
